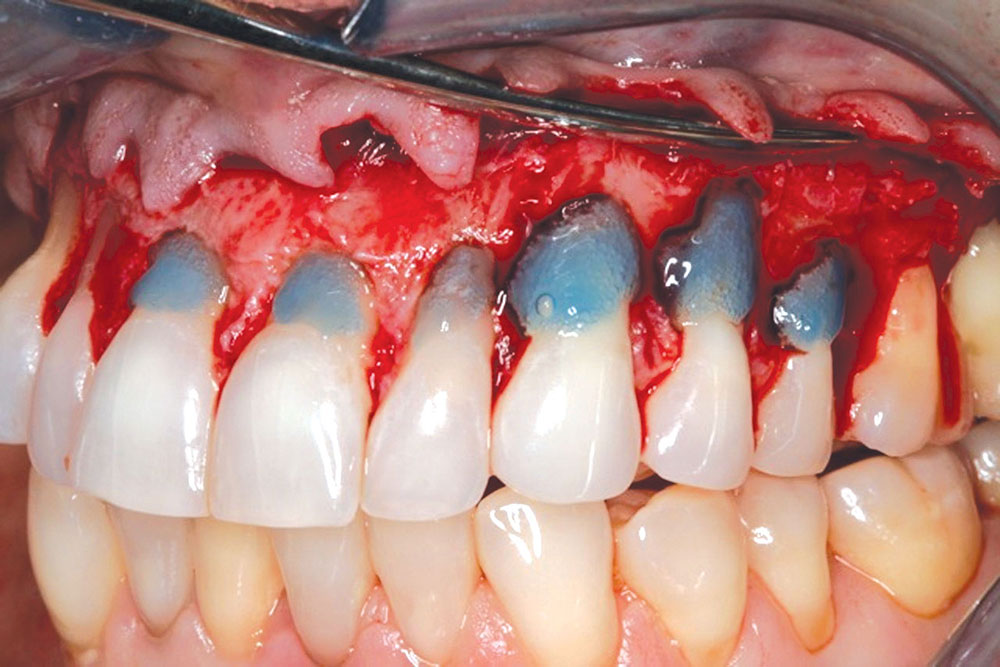
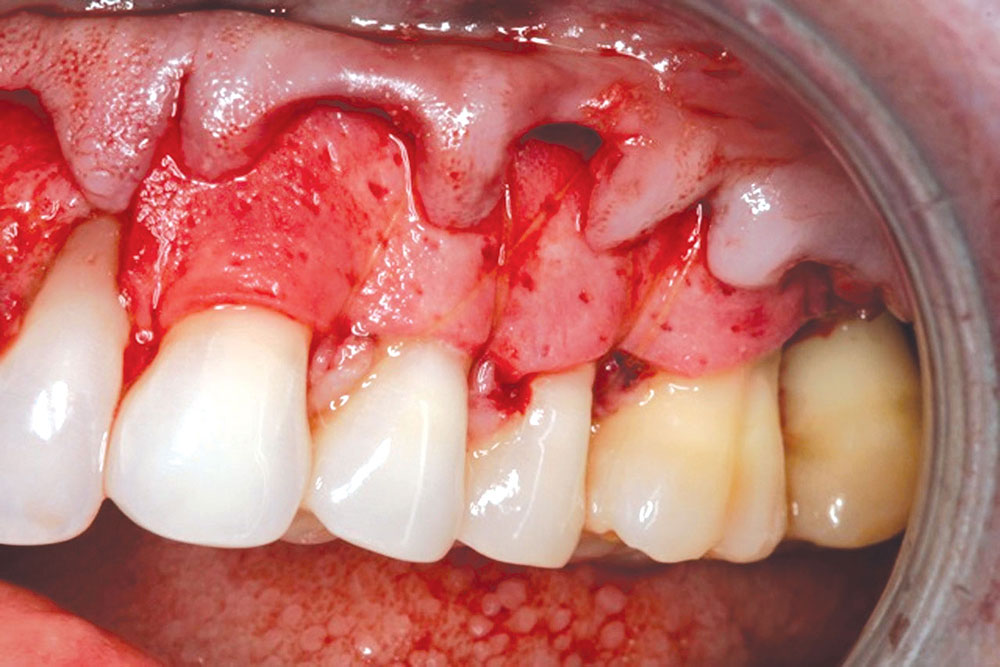
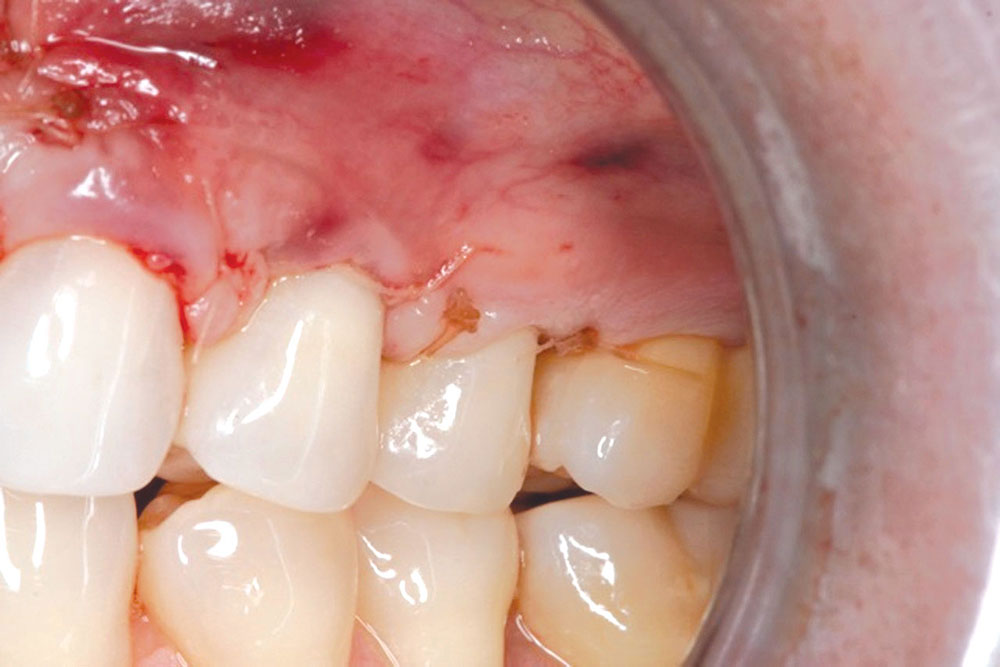
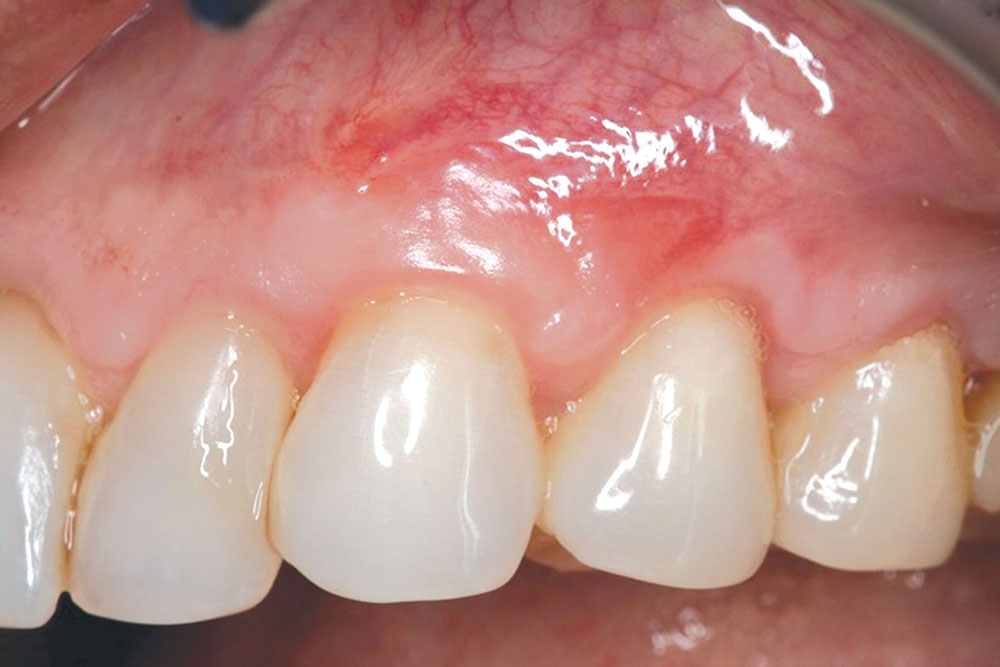
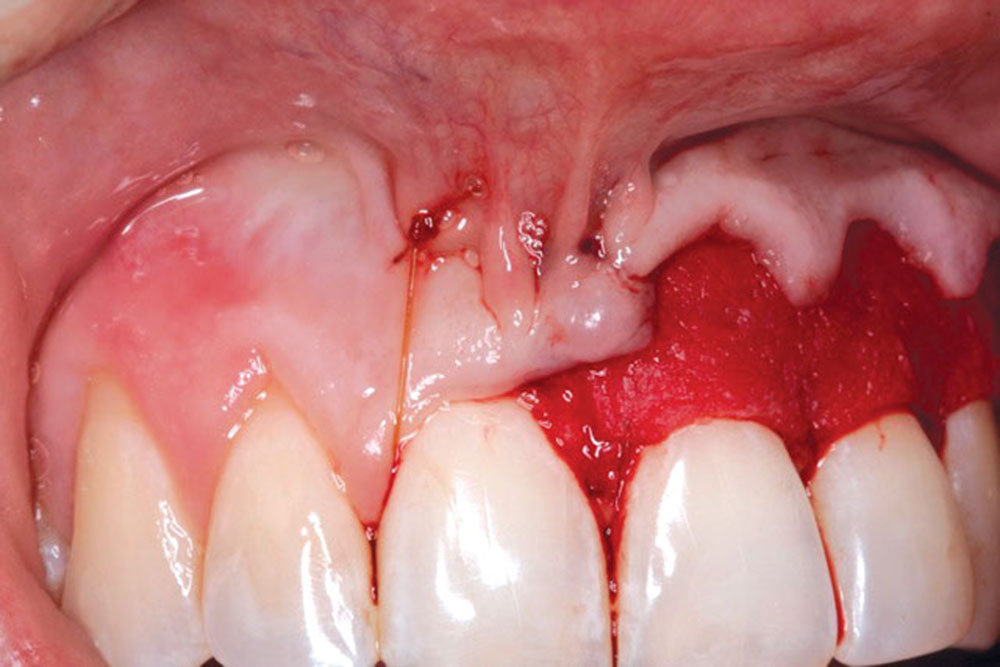
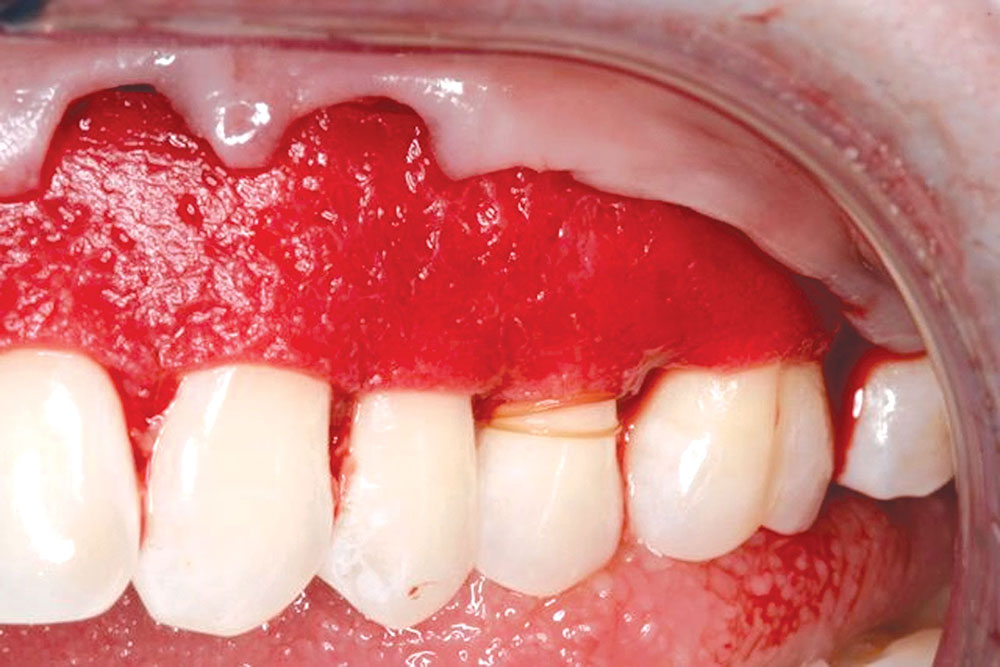
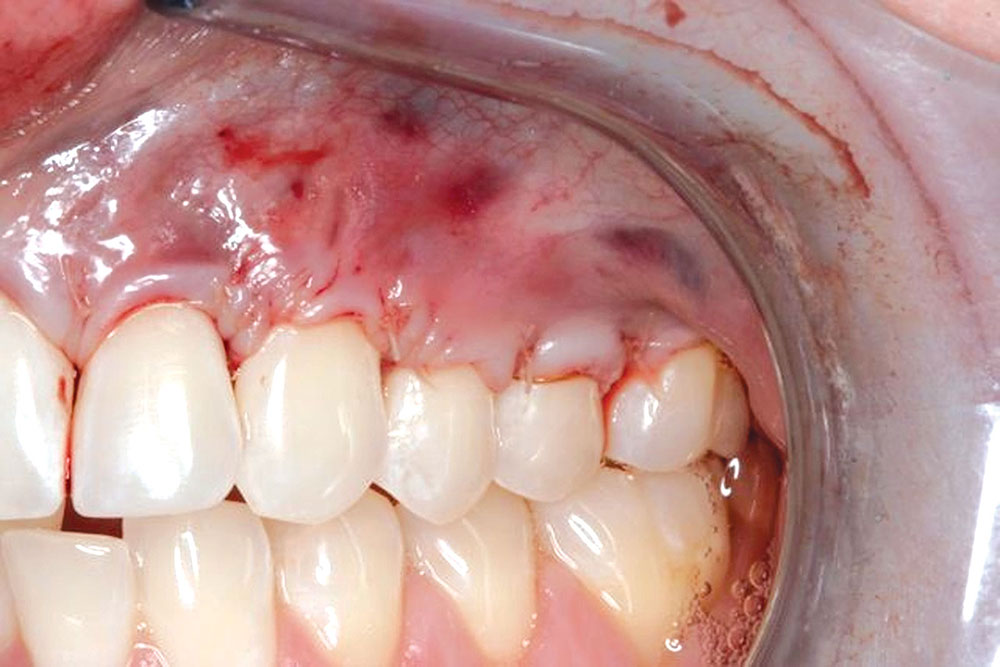
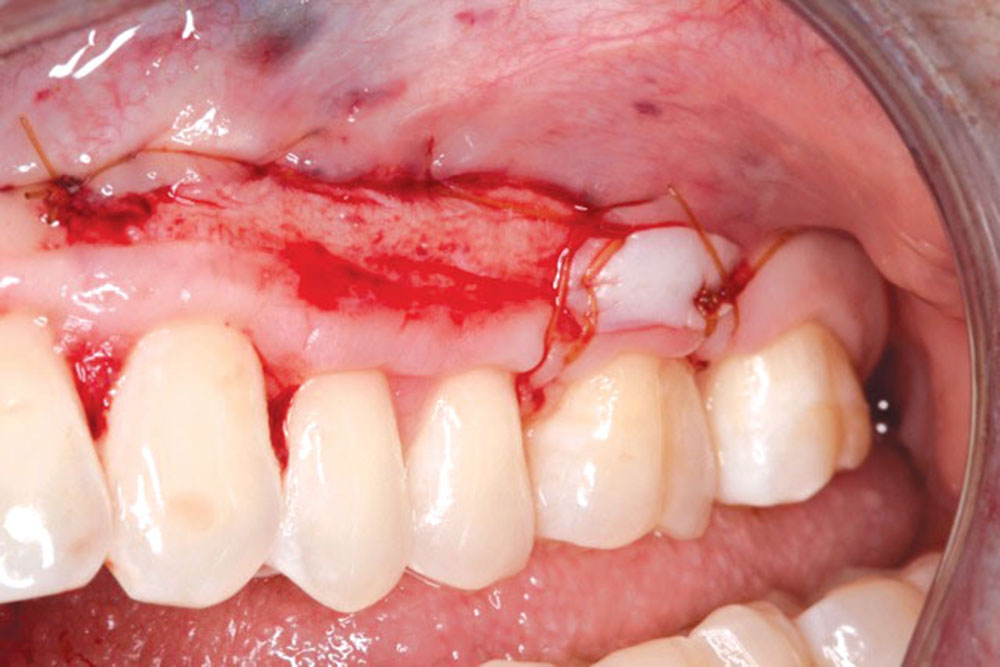
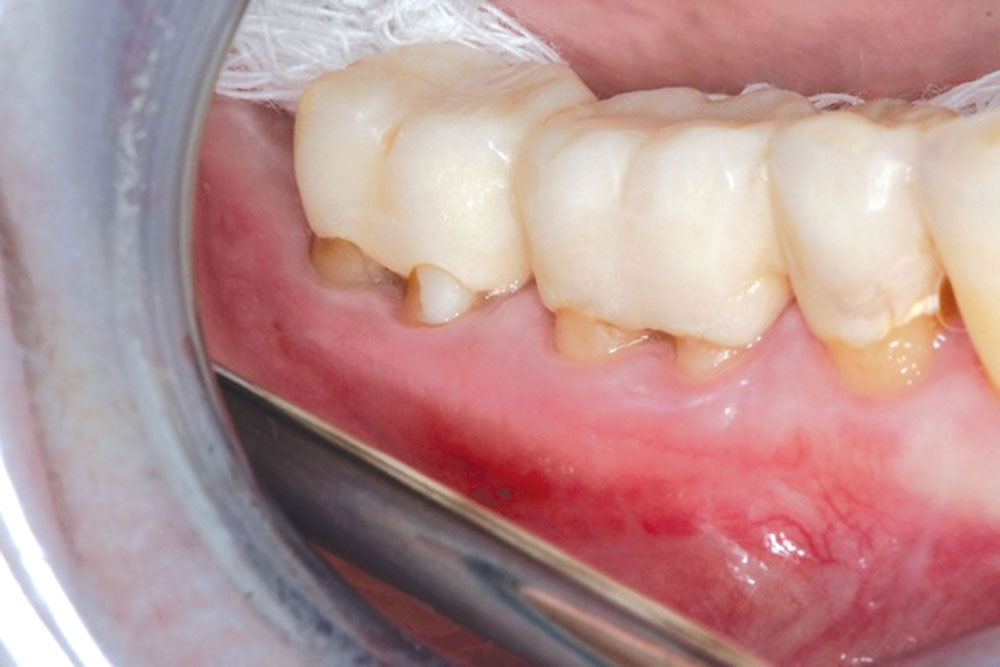
The Use of PerioDerm™ for Root Coverage and Correction of Insufficient Attached Gingiva
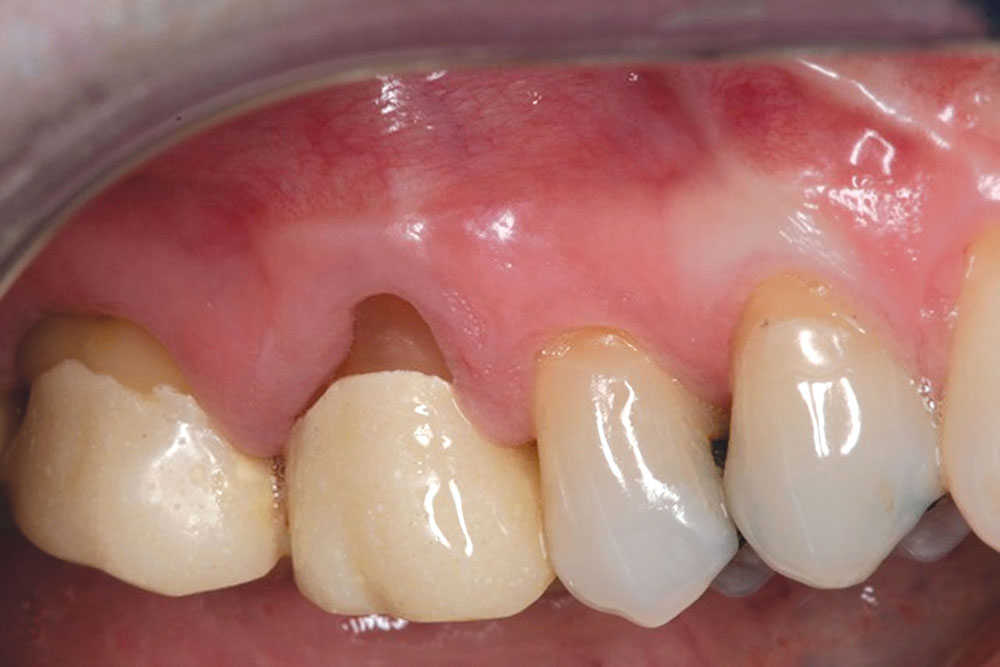
The objective of this article is to demonstrate the benefits of an acellular dermal matrix called PerioDerm™ Acellular Dermis (DENTSPLY Tulsa Dental Specialties; Tulsa, Okla.) in correcting recession and adding connective tissue during periodontal-restorative comprehensive treatment.1,2 It has long been established that connective tissue is an integral factor in the protection of the underlying periodontal foundation. Connective tissue tends to be tenacious in makeup and have far less vascularization than mucosa. It prevents bacterial infiltration to the underlying supportive periodontal tissues, and in restorative applications, it adds stability to gingival areas during impression taking and cementation of restorations. Though the quality of tissue is critical, it is also important that the tissue is bound down to either tooth surface or bone to serve as a supportive mechanism for protection of the periodontium.
The benefits of connective tissue have been well documented since 1968, in an article by Sullivan and Atkins.3 During the early years, palatal tissue was the main donor to harvest connective tissue, and today, there continue to be instances where palatal tissue would be the recommended tissue of choice. That being said, I have found PerioDerm to be a very user-friendly material for the addition of connective tissue. The cases presented here will show that PerioDerm can be a benefit when used to cover root surfaces, or to simply increase connective tissue for support of restorations.
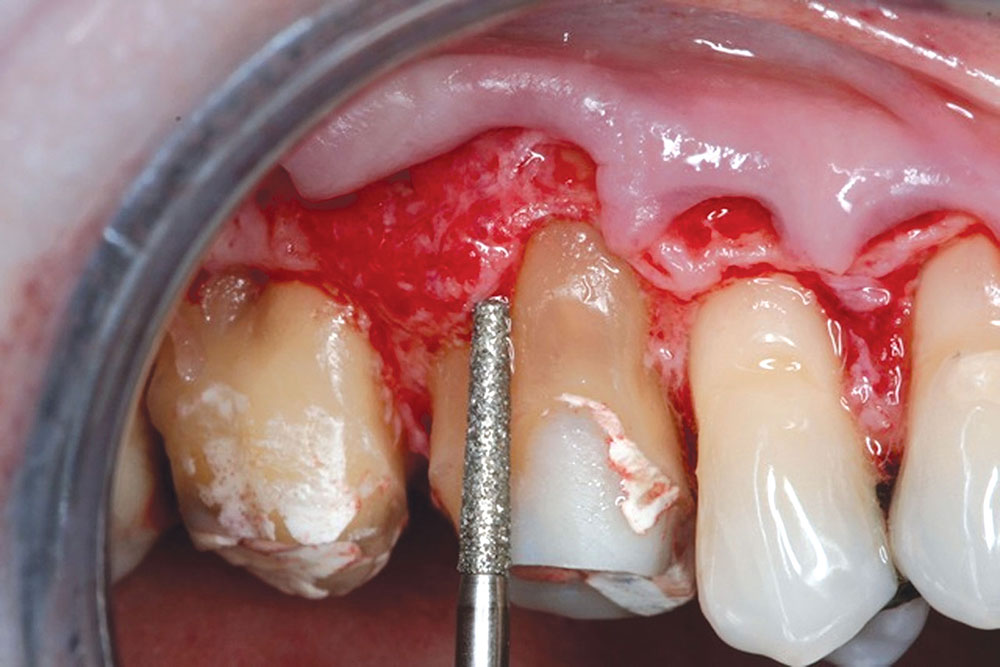
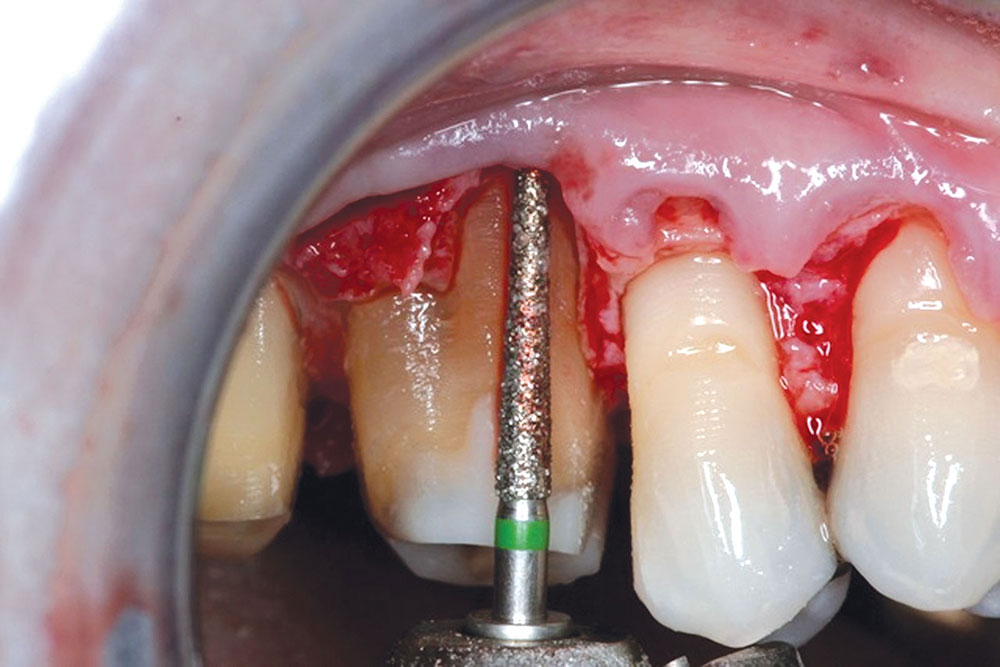
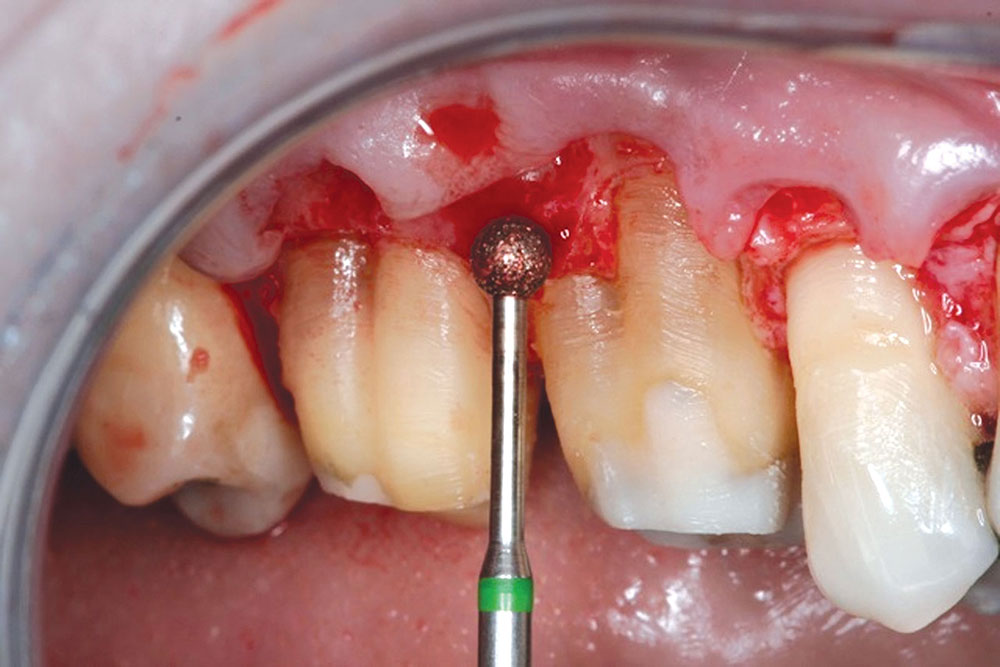
Techniques for the use of PerioDerm that may differ from standardized procedures, such as tunneling, will also be shown.4,5 It is my opinion that visibility via flap procedures of the recipient bed is a key factor in treating all periodontal issues that could have caused previous, or may cause future, breakdown of the periodontium. This article will illustrate the benefits of simple secondary procedures to remove any muscle fibers or mucosa present at the gingival collar, and a technique to position these tissues at the apical portion of the PerioDerm.
The benefits of PerioDerm in relation to other acellular dermal matrices are as follows:
- User-friendly.
- Short hydration period.
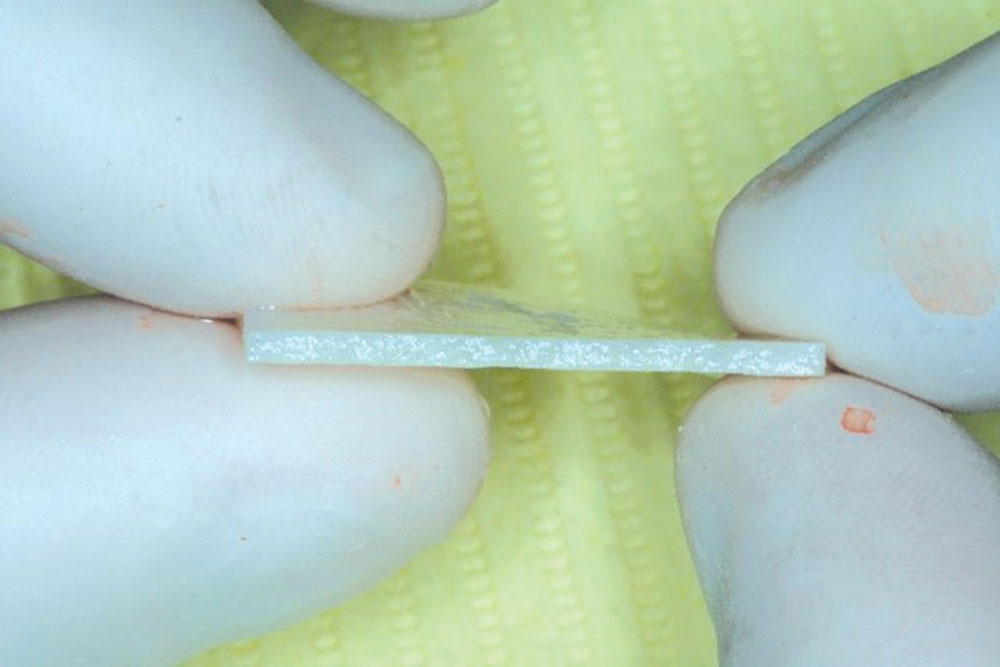
- Can be trimmed after moistened. It can be placed in the mouth and trimmed to the contour of each cementoenamel junction (CEJ) using surgical scissors.
- Sticks to the tooth and not the glove of the surgeon.
- Suture easily passes through the material.
- Uniform thickness of the material. I recommend using thick PerioDerm, instead of the thin variety.
- Very compatible with existing tissue.
- Upon reentry, the existing tissue appears to have all the characteristics of connective tissue. However, without histology, this is nothing more than a clinical observation. Though only an observation, it is a critical advantage as the tissue serves to protect the underlying periodontal tissues.
Several of the cases presented in this article deal with the correction of furcations on natural teeth that will not be restored. Below is the protocol for dealing with sensitivity during treatment.
DESENSITIZING TREATMENTS
Surgery
Super Seal® Dental Desensitizer Liner (Phoenix Dental, Inc.; Fenton, Mich.) should be used after suturing. The teeth must be dry. One drop is placed on each tooth and lightly air-blown dry after 30–40 seconds. Repeat three to four times. If the teeth have been severely barreled into the furcation, a drop of prednisolone 1% is also placed on the teeth.
The patient is given PreviDent® Gel (1.1% sodium fluoride) (Colgate® Oral Pharmaceuticals; New York, N.Y.) to mix with water and rinse with at home twice daily for one minute.
Week 1
The patient is scaled with a universal implant scaler (double end) because it is made with plastic and more comfortable for the patient.
The patient is then polished with Colgate® Sensitive Pro-Relief™ desensitizing paste (Colgate Oral Pharmaceuticals). The wooden end of a cotton-tipped applicator is used to spread the paste interproximally.
If the patient cannot brush, a drop of prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension USP 1% is placed on the teeth. The patient rinses with Sultan Topex® in-office fluoride rinse (Sultan Healthcare; Hackensack, N.J.) for one minute. The patient is to rinse two times a day with the PreviDent solution, which is expectorated after use. The patient cannot eat, drink or rinse for 30 minutes after use.
If the patient is able to start brushing, a drop of prednisolone is placed on the teeth. PreviDent® Varnish 5% sodium fluoride (Colgate Oral Pharmaceuticals) or 3M™ CavityShield™ 5% sodium fluoride (3M™ ESPE™ St. Paul, Minn.) is also placed on the teeth. The patient is instructed to brush it off in four hours with regular toothpaste. The patient is to start brushing with PreviDent gel twice a day for one minute after they have brushed with regular toothpaste. PreviDent gel is to be expectorated after brushing and the patient cannot eat, drink or rinse for 30 minutes after use.
Following Weeks
All treatments are based on whether the patient is allowed to brush.
If the patient cannot brush, a drop of prednisolone is placed on the teeth. The patient is to keep rinsing two times a day with PreviDent. The patient rinses with Sultan Topex in-office fluoride rinse for one minute.
TIPS TO AVOID SURGICAL FAILURE
- Avoid perforation of the flap. Feel for any exostoses or tori; if found, a full-thickness flap should be initiated to avoid perforation of the tissue. After passing the protrusion that could cause a perforation, split the tissue, leaving the periosteum on the bone.
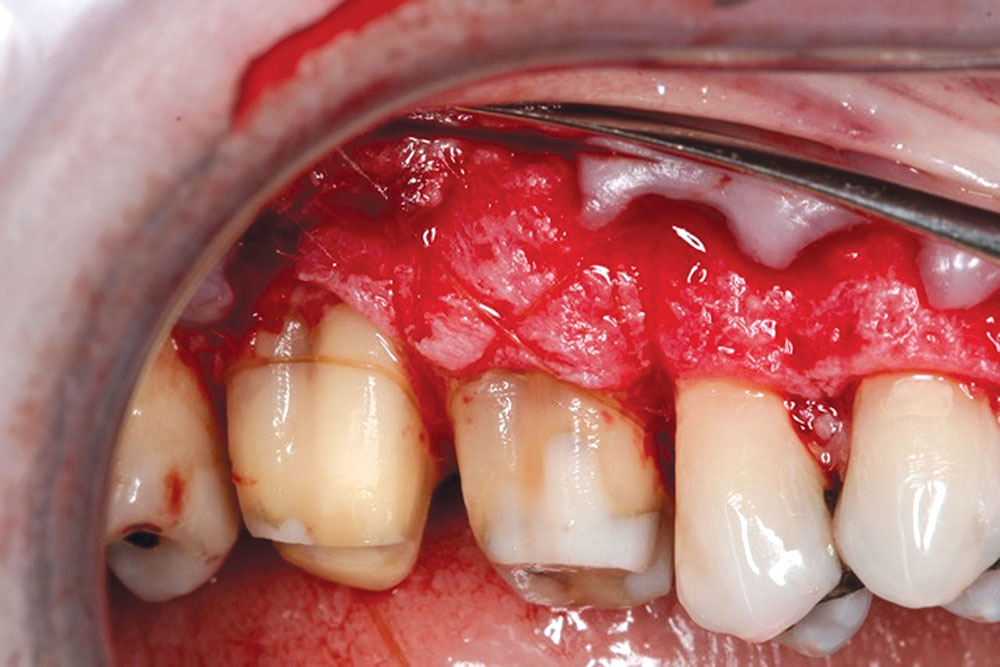
- Upon releasing the flap, make sure it is tension-free when advancing it coronally. Tension could cause necrosis of the flap and possible failure.
- When suturing the flap, sutures should be positioned to keep the flap in place without advancing it. Sutures should not place tension on the flap.
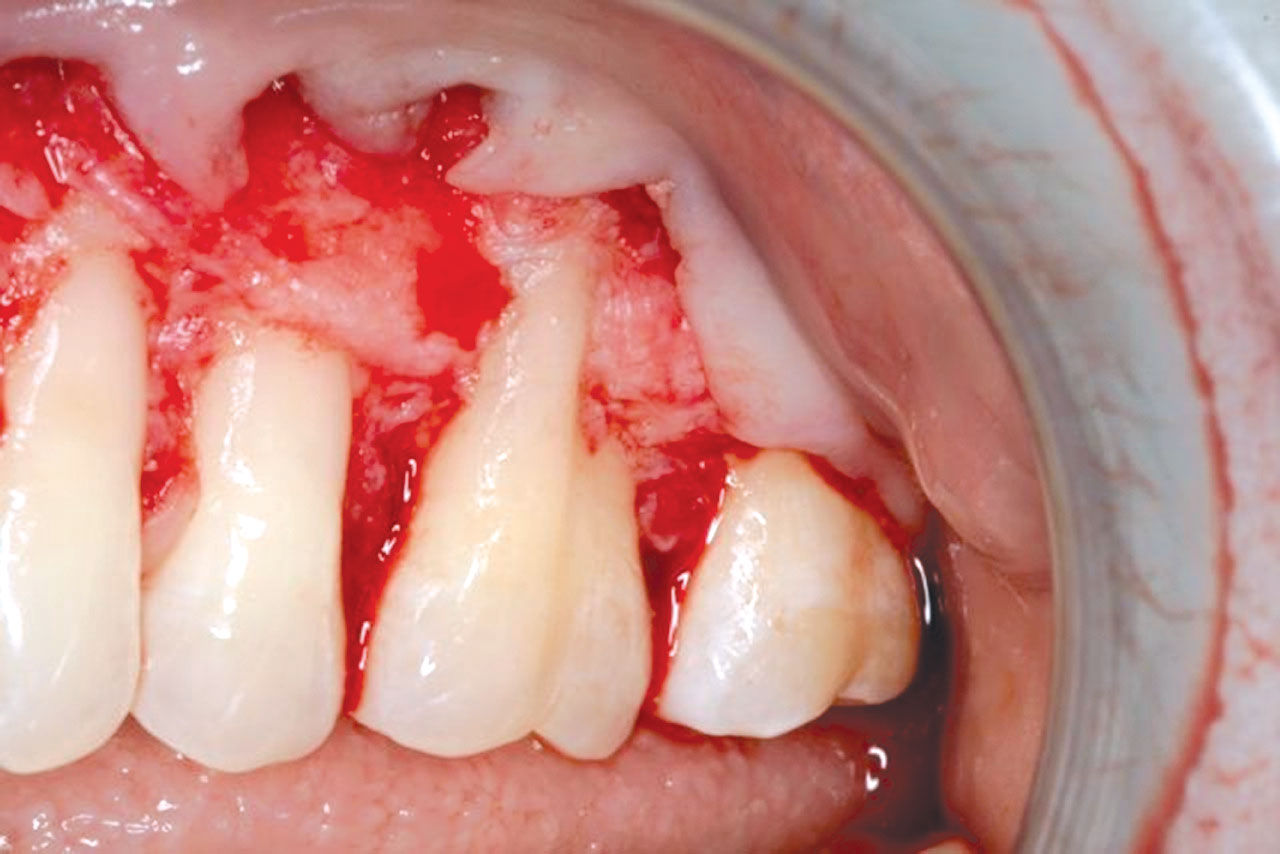
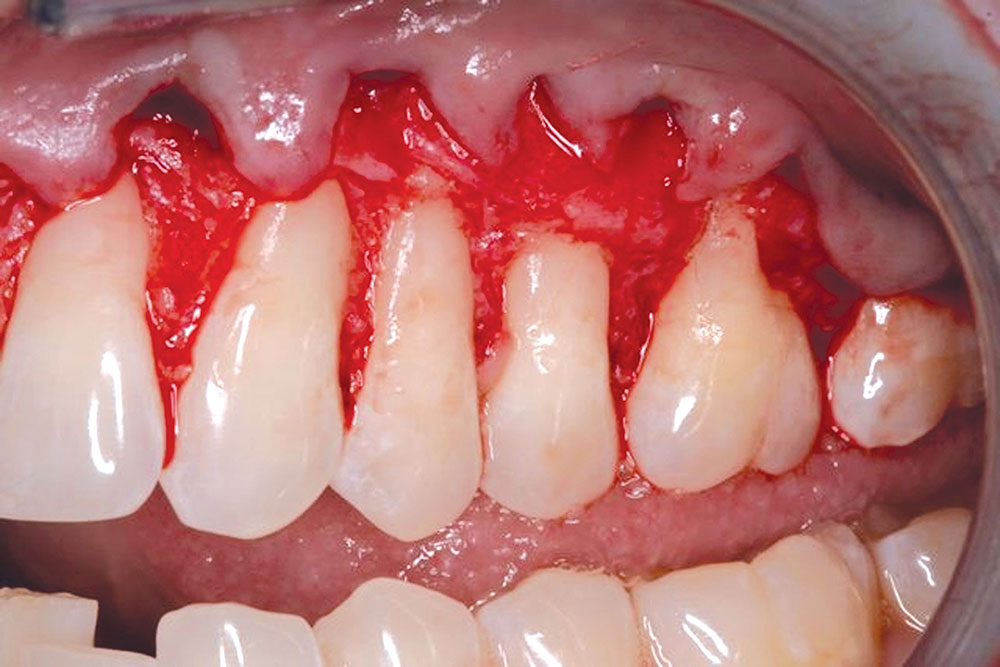
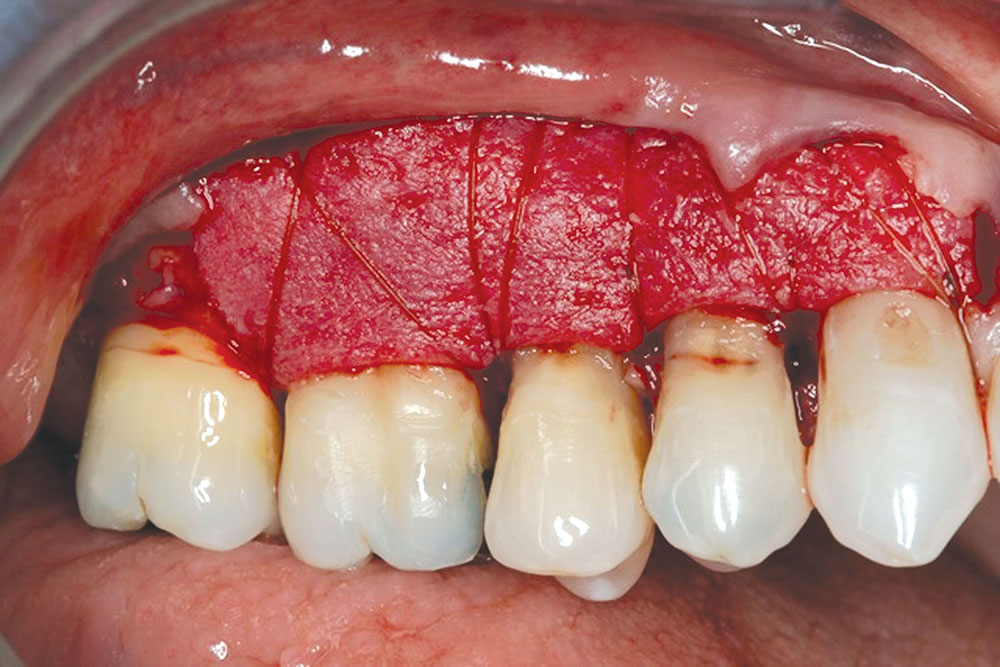
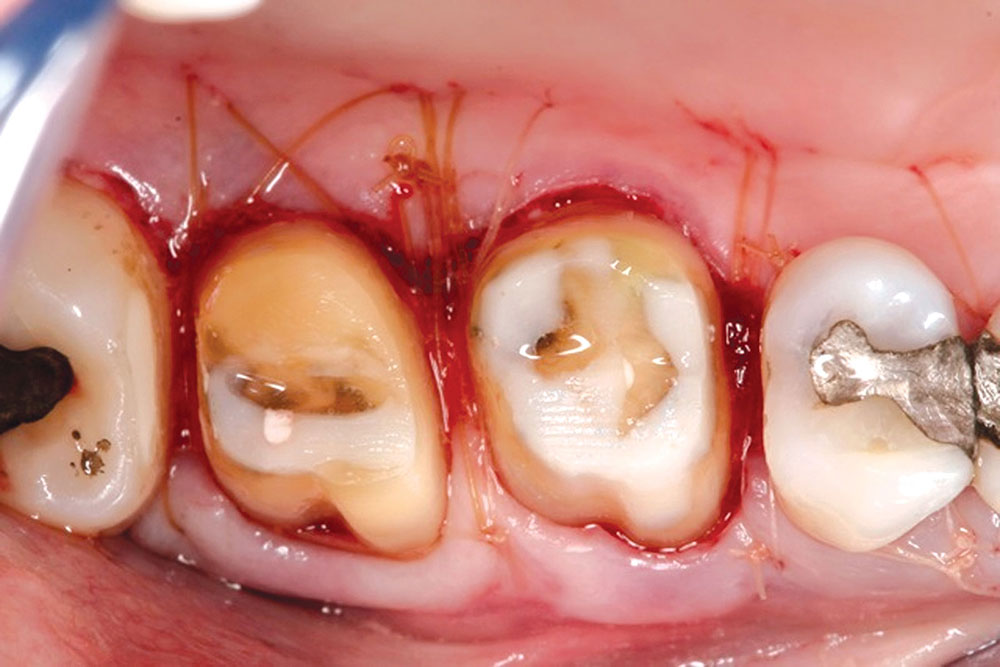
- The graft, i.e., PerioDerm, should have 100% coverage by the flap.
- The patient should avoid brushing the area with a toothbrush to prevent accidental pulling of the sutures and necrosis of the flap.
TIPS FOR HOME CARE
- Following surgery, the patient will use 0.2% chlorhexidine twice daily. The patient should use this liquid first thing in the morning, rinsing for one minute and then expectorating. The same procedure should be repeated before bedtime.
- The PreviDent gel should be placed on the teeth where the teeth meet the gum line. It should be applied to these areas for one minute and then expectorated.
- The patient can rinse with water several times a day to remove debris.
- The patient should not eat on the side where the procedure was undertaken.
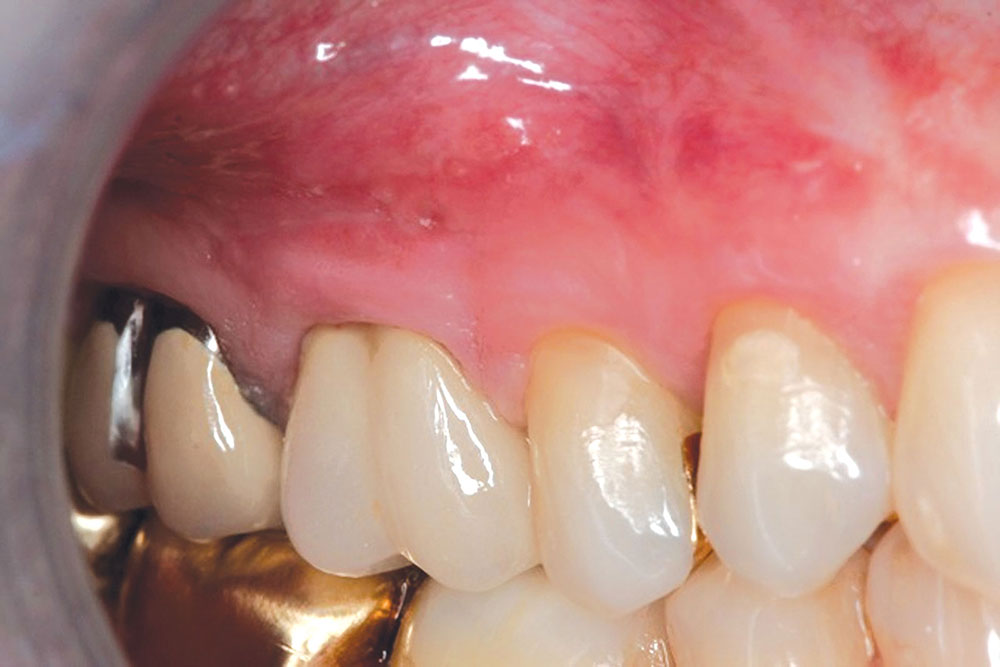
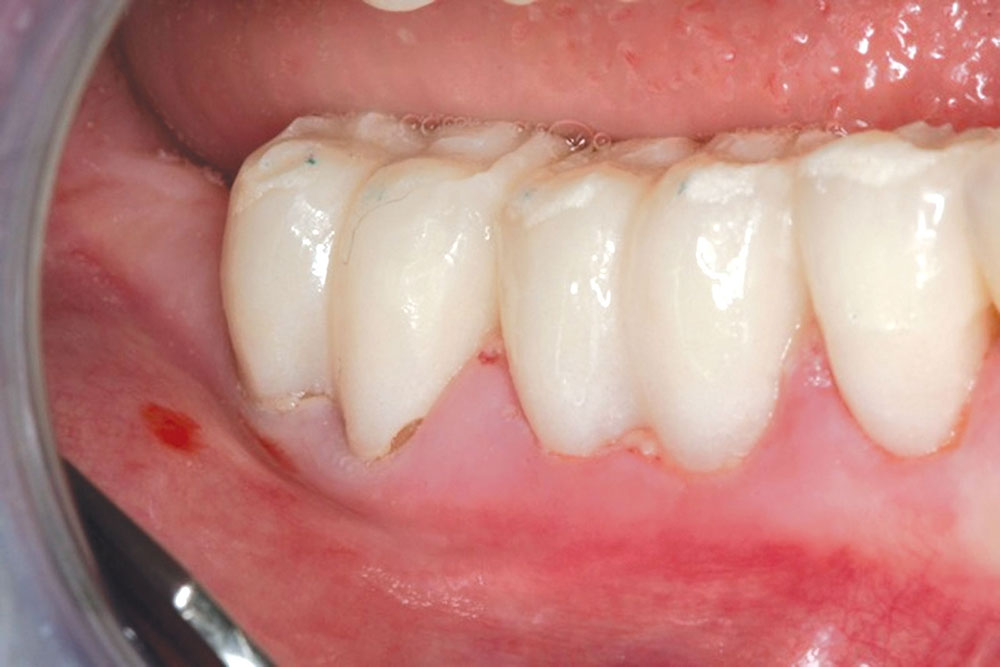
- Due to the very compatible nature of the patient’s tissue and PerioDerm, the patient can in many cases start to brush the teeth during the second week using the Braun Oral-B® toothbrush (Procter & Gamble; Cincinnati, Ohio). The patient should use the toothbrush only on the tooth surface, stopping at the gingival collar. NOTE: The key to the timing of the brushing depends on the adaptation of the flaps during healing. If the tissue appears well-adapted, the sutures can be removed and brushing initiated.
- Flossing can begin once the sutures are removed and the flaps are closely adapted to the tooth surface.
Connective tissue is an integral factor in the protection of the underlying periodontal foundation. … Though the quality of tissue is critical, it is also important that the tissue is bound down to either tooth surface or bone to serve as a supportive mechanism for protection of the periodontium.
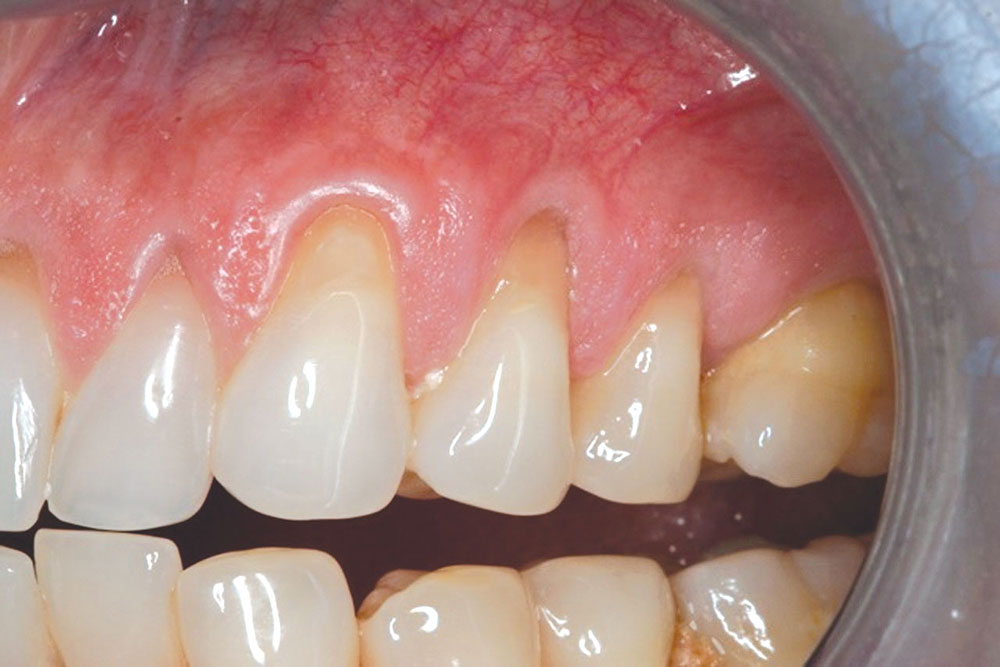
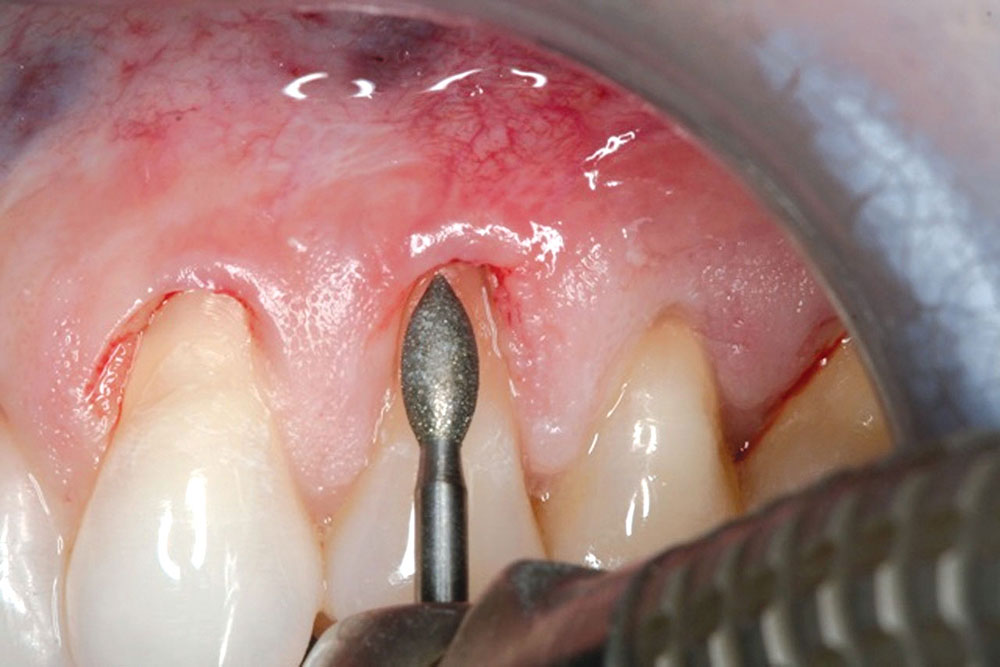
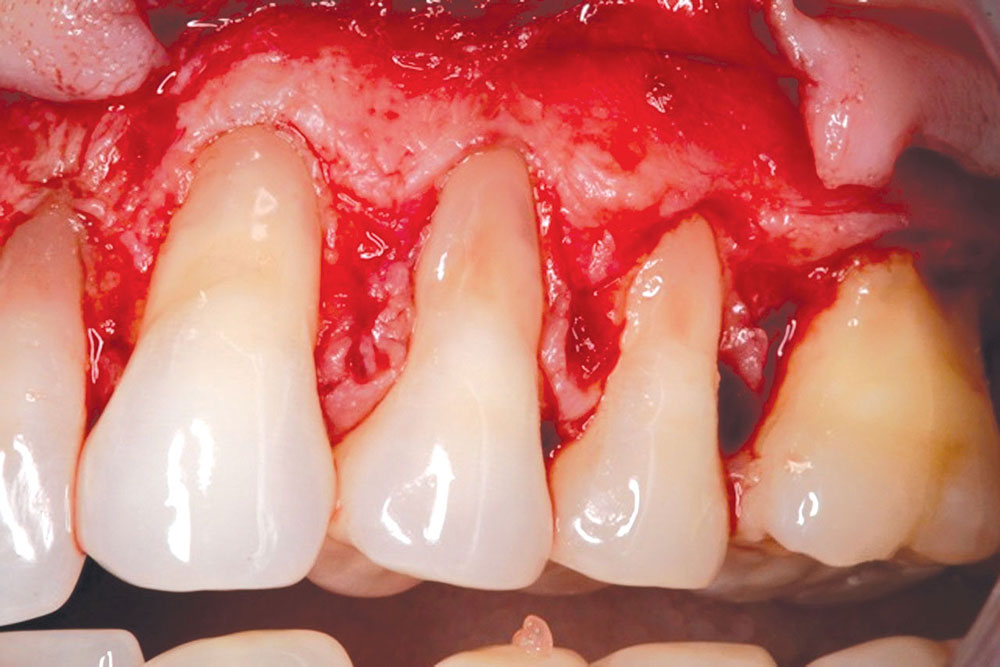
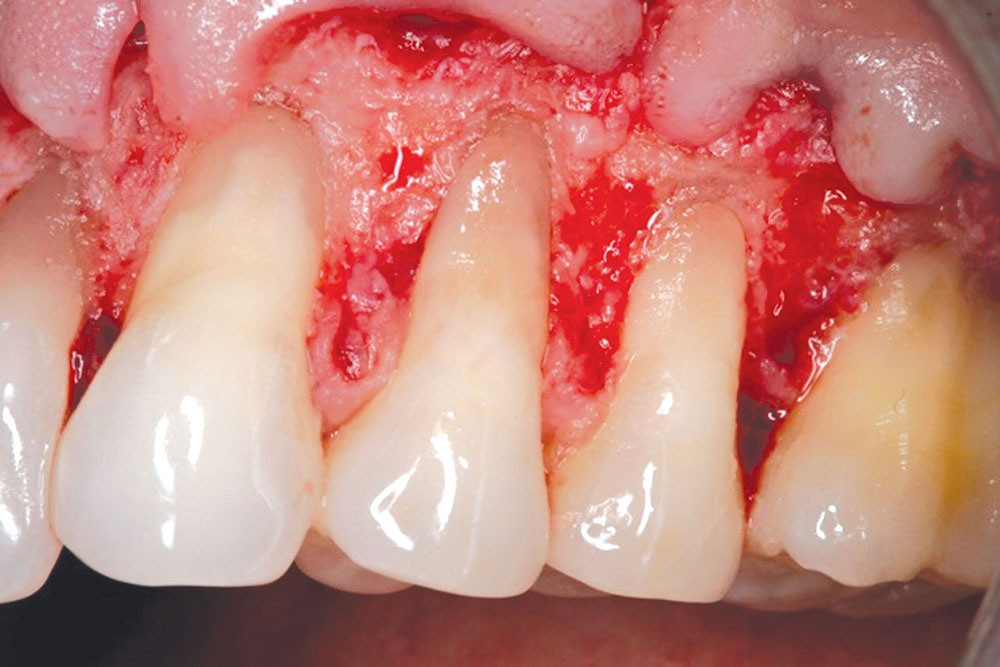
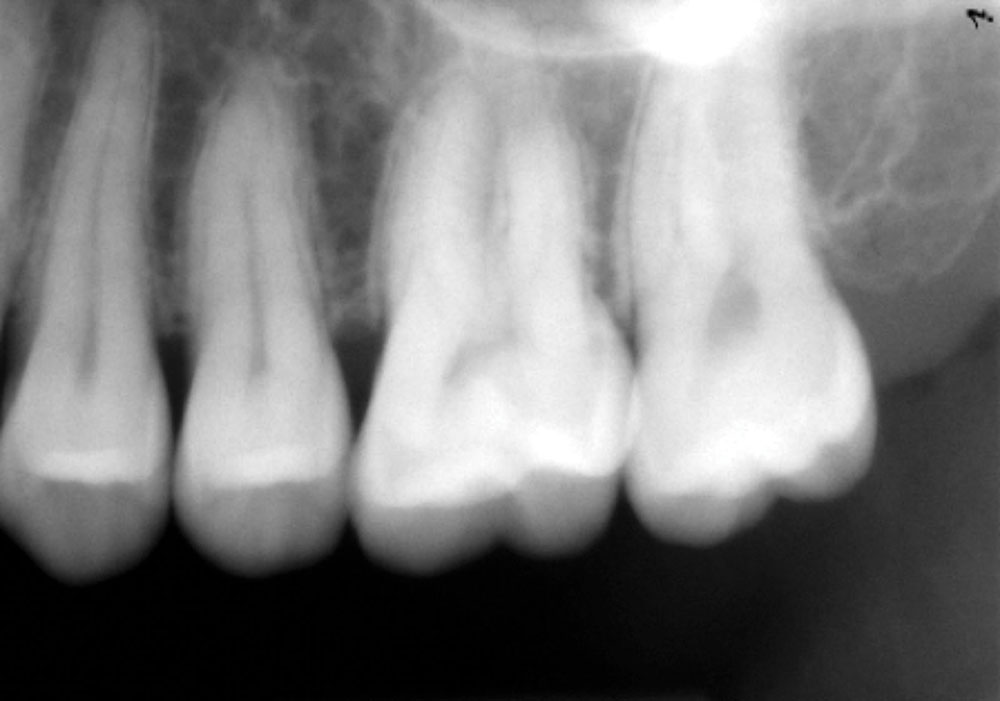
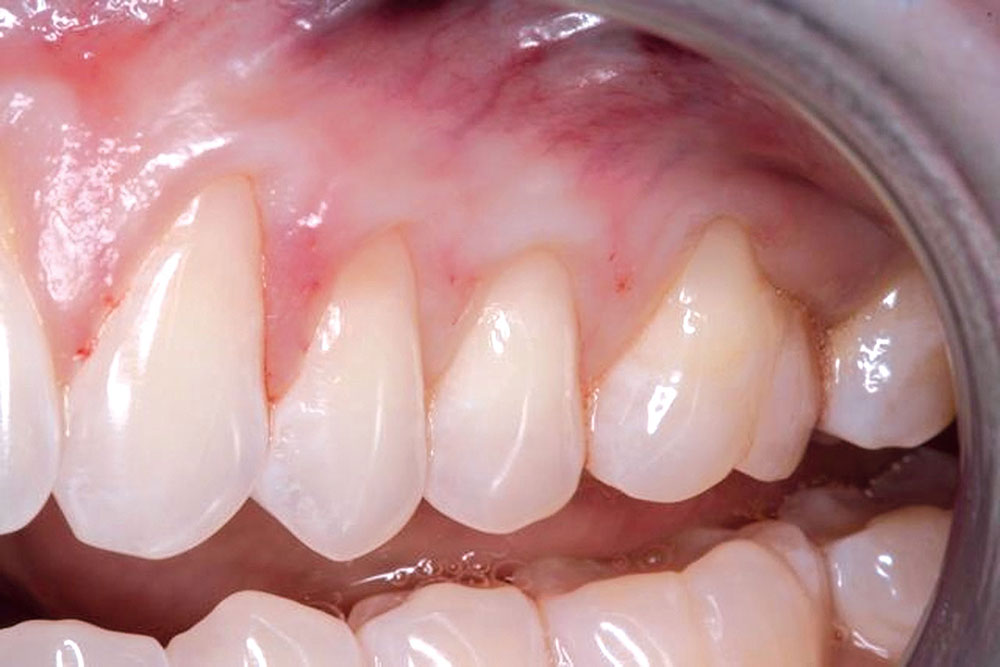
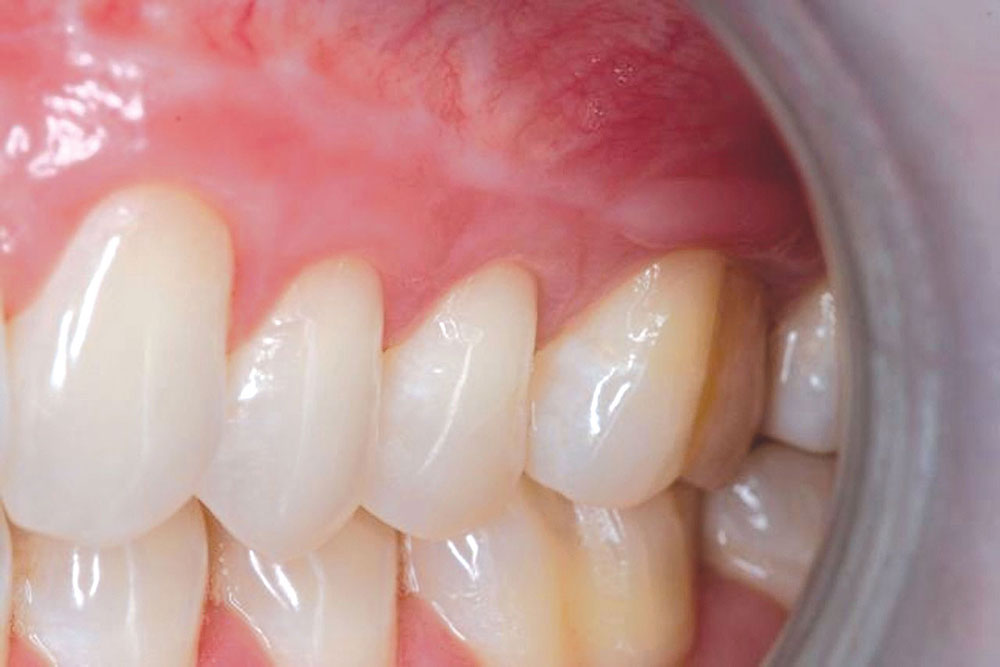
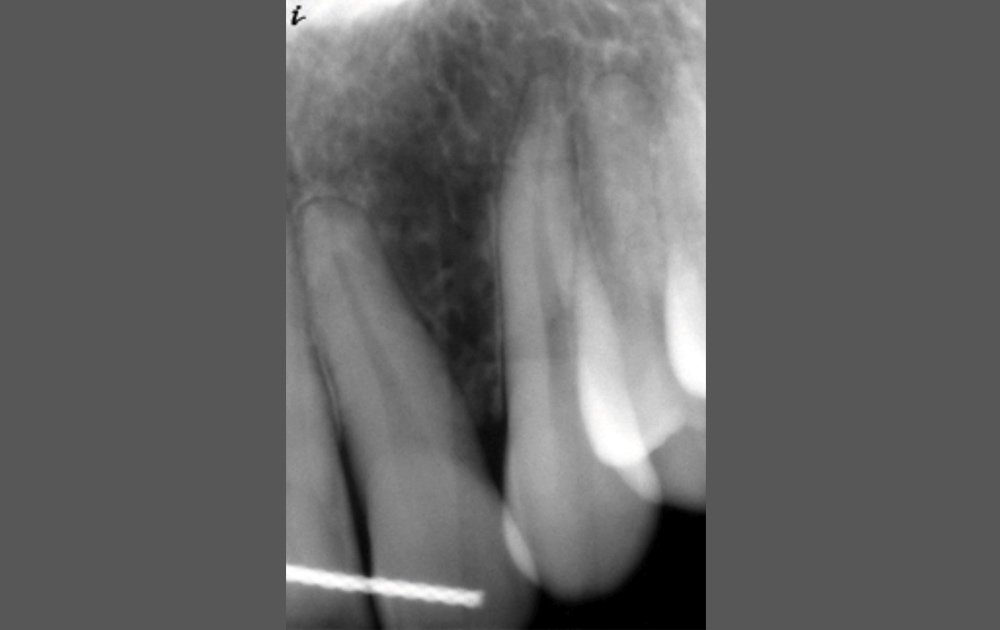
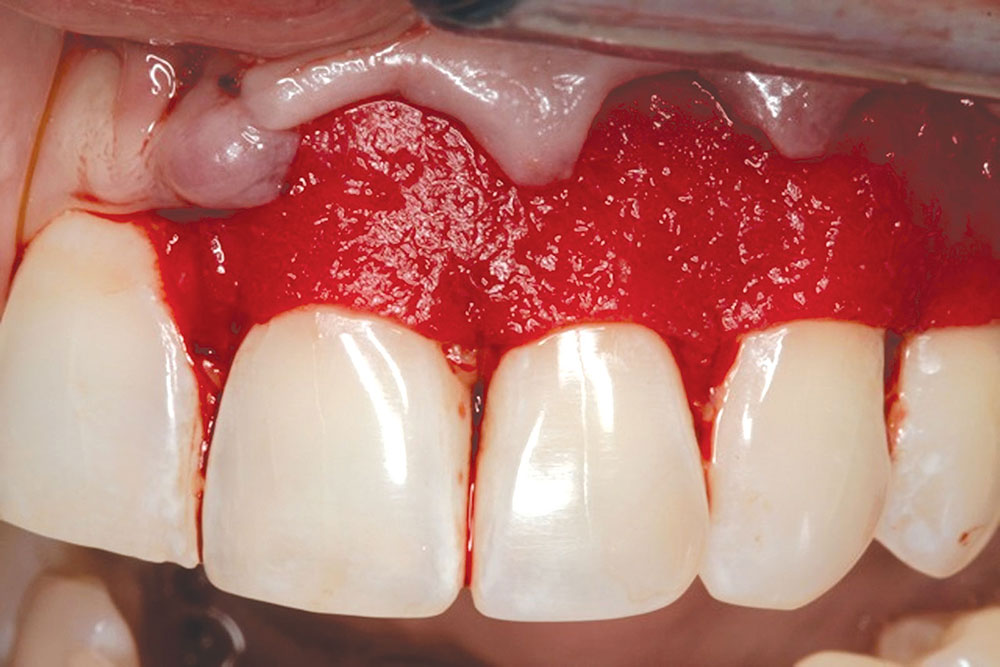
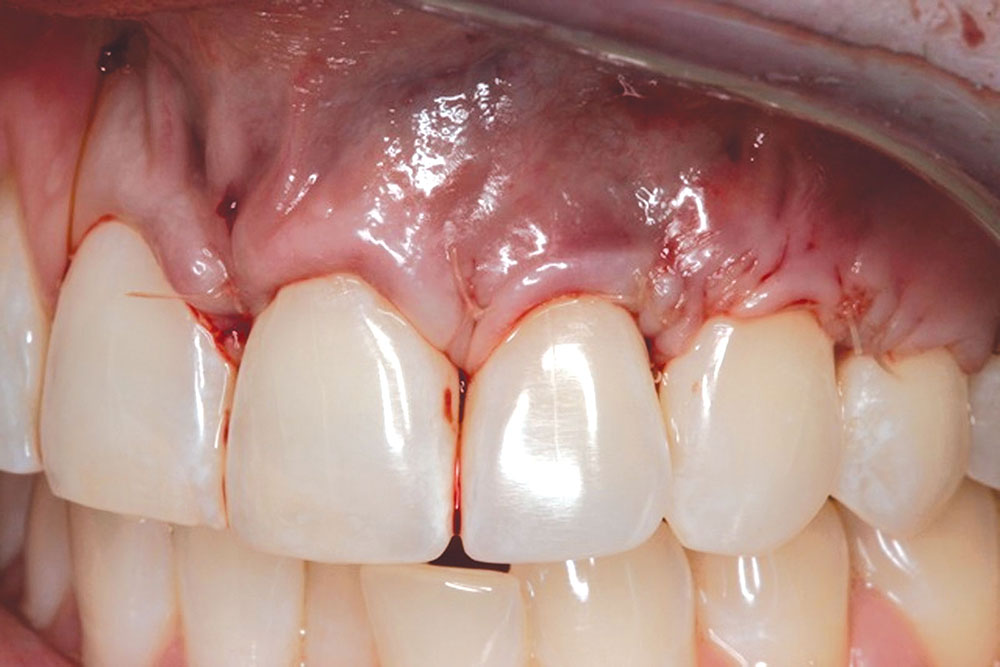
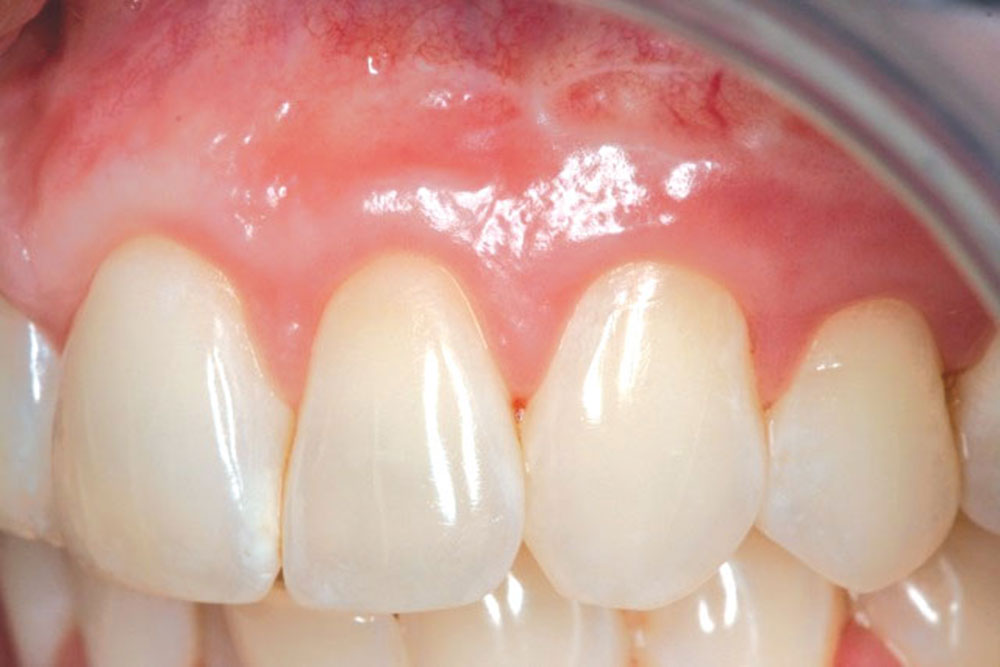
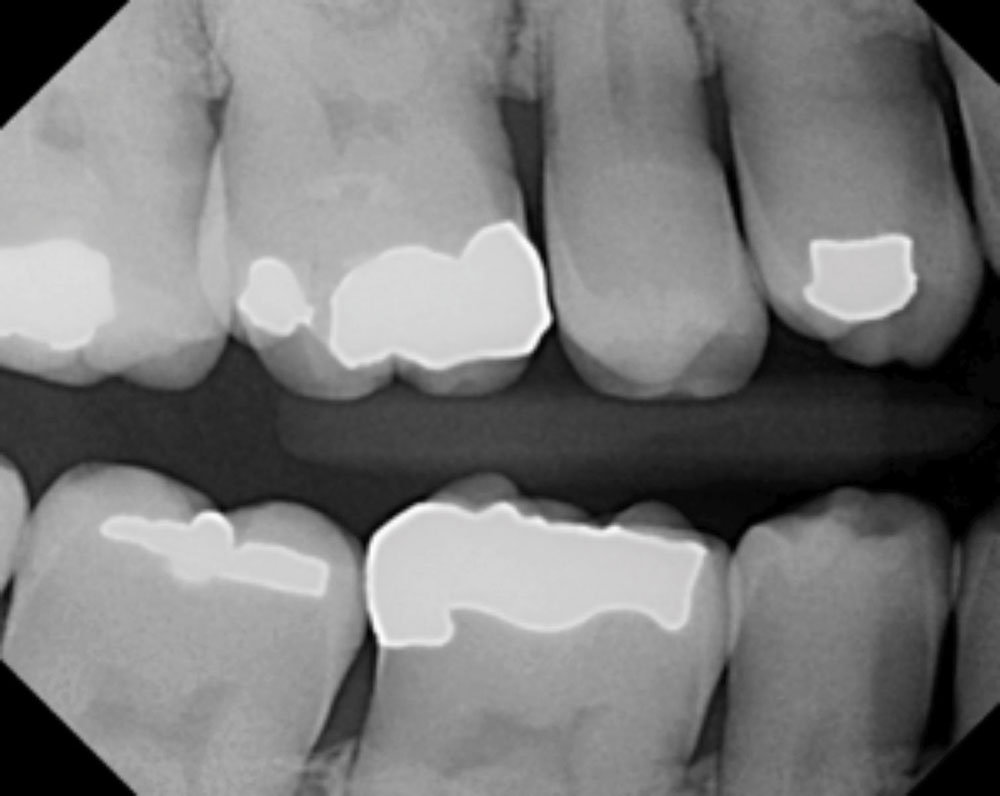
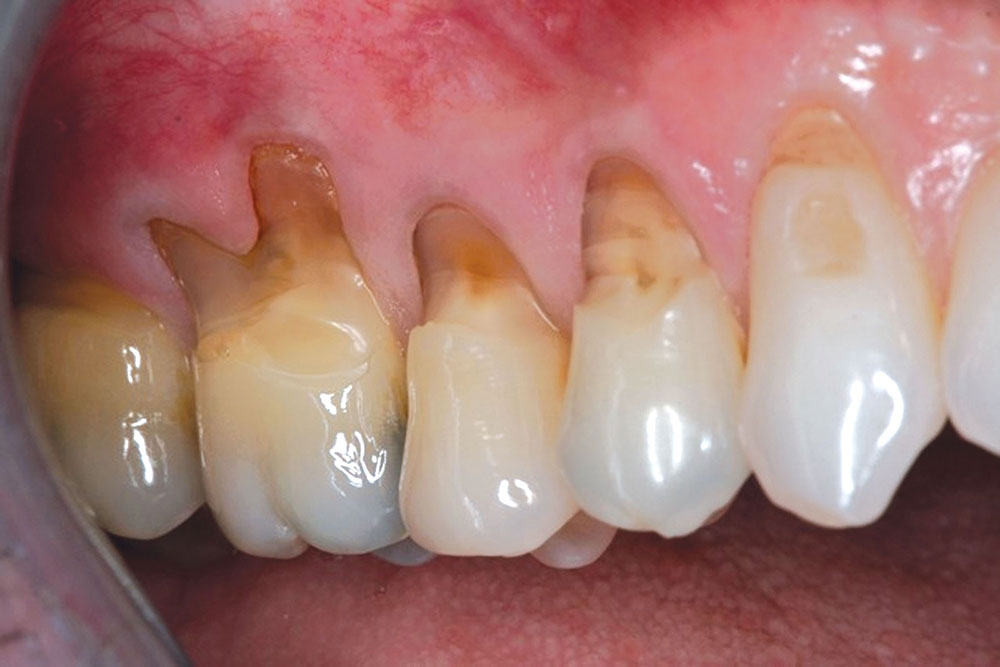
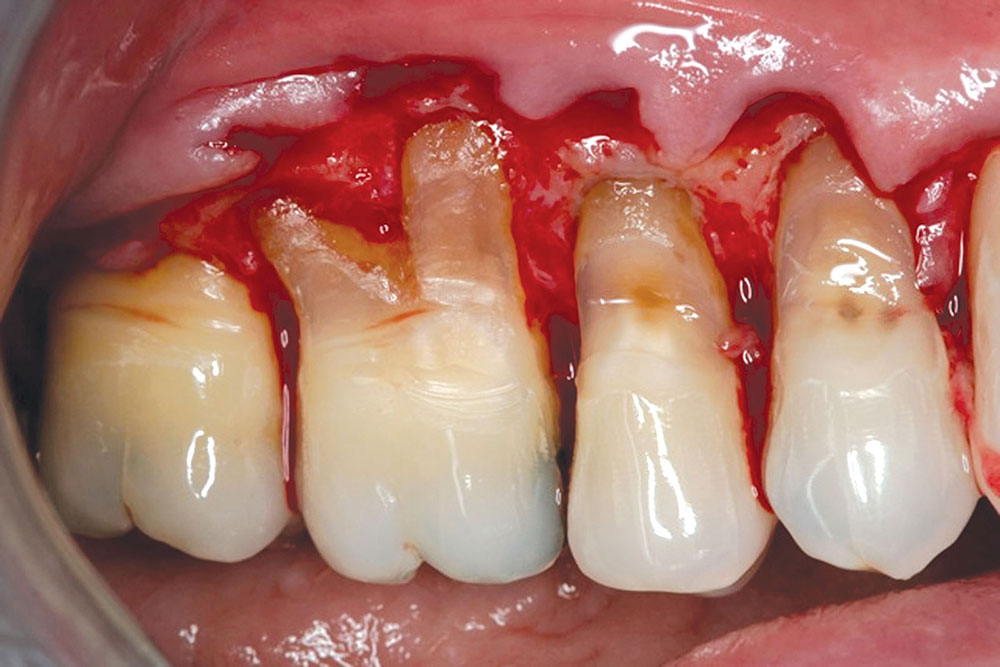
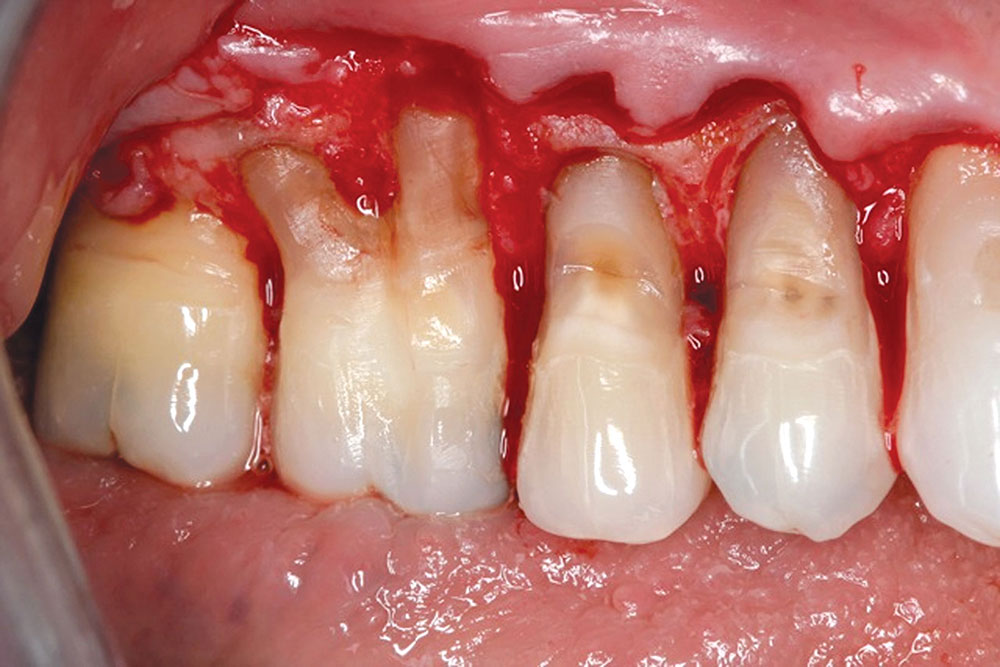
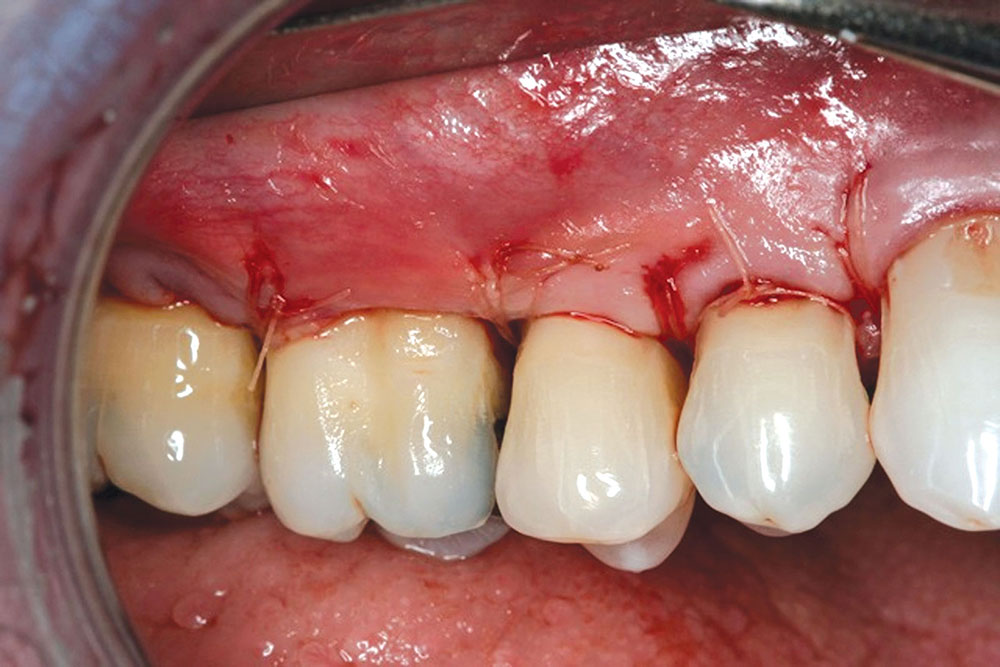
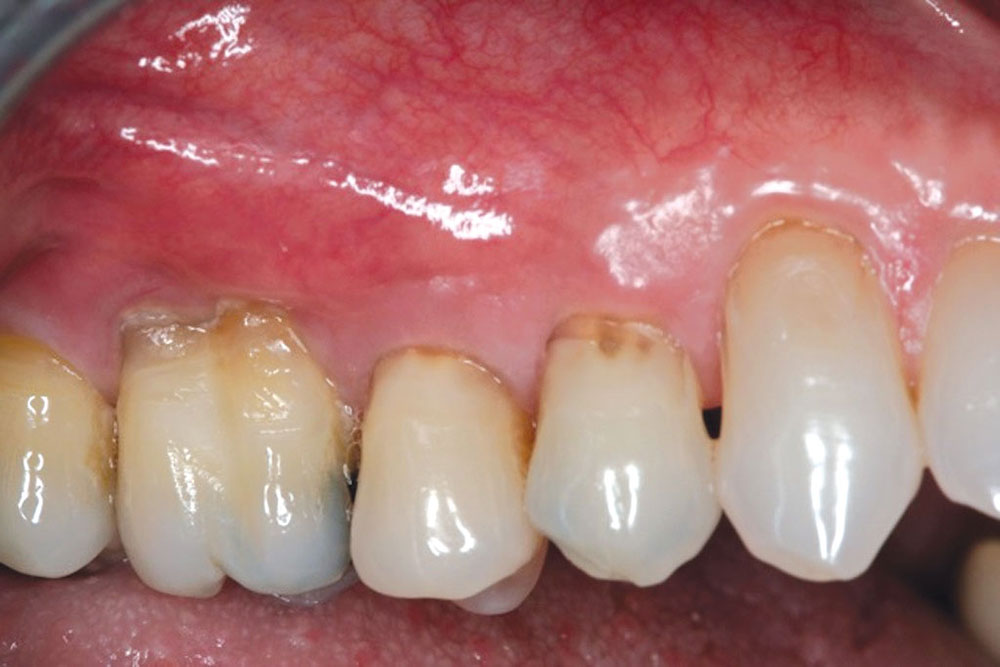
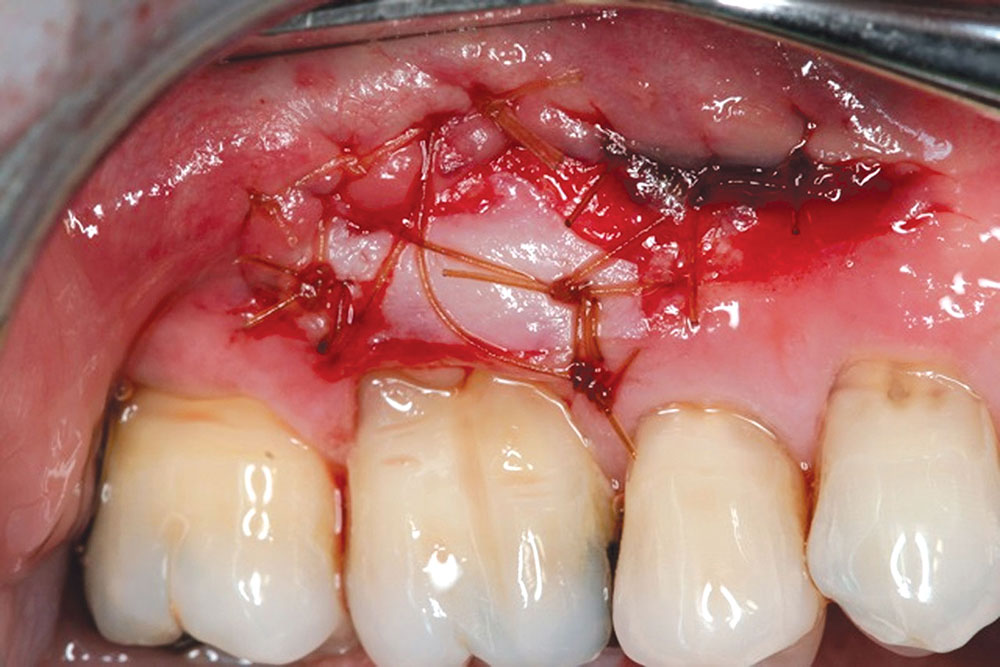
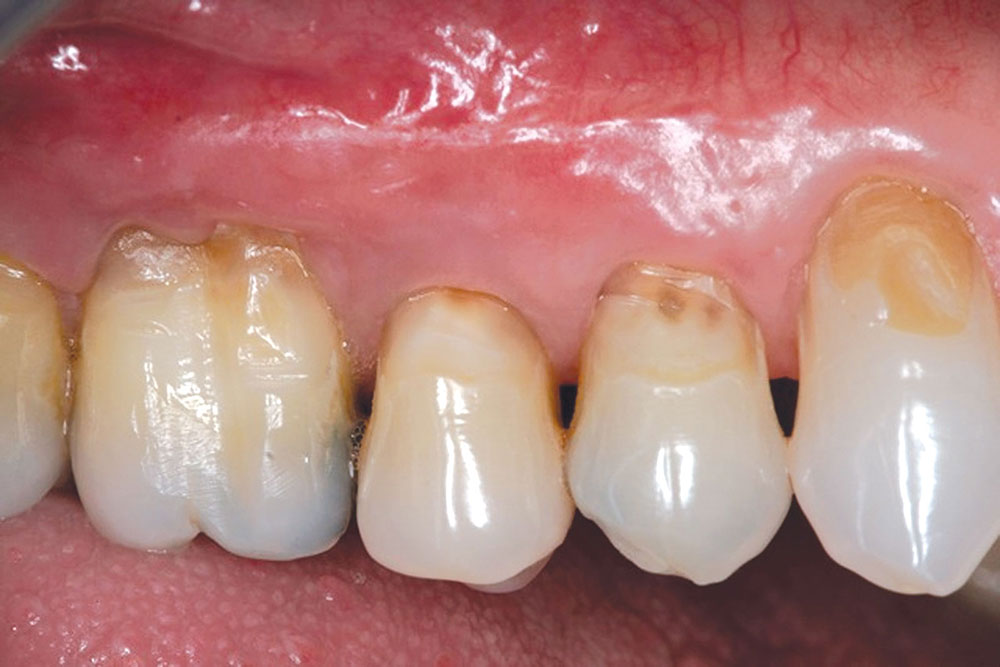
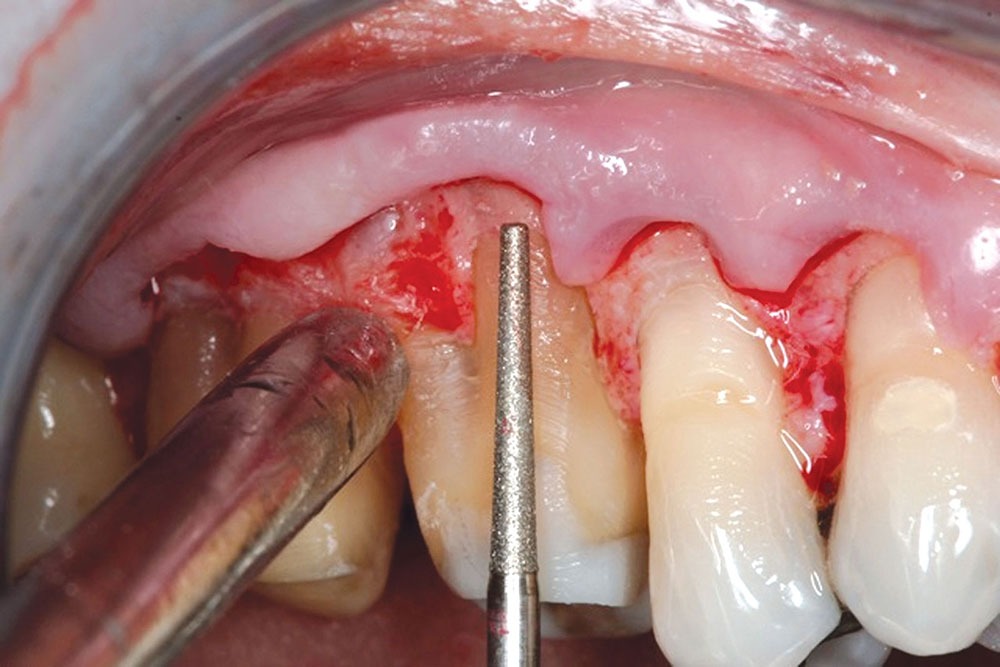
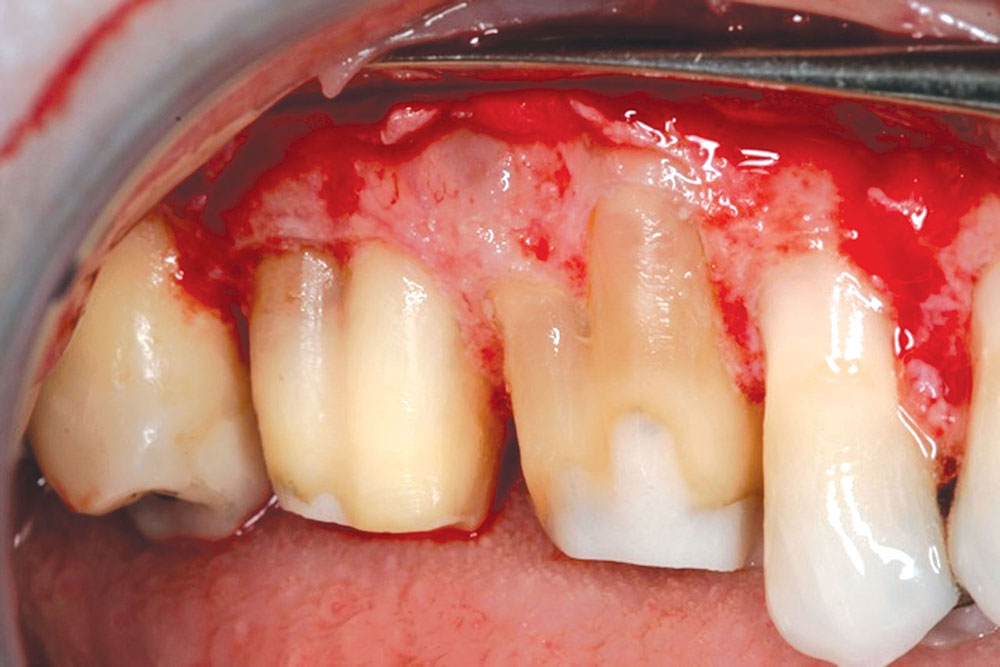
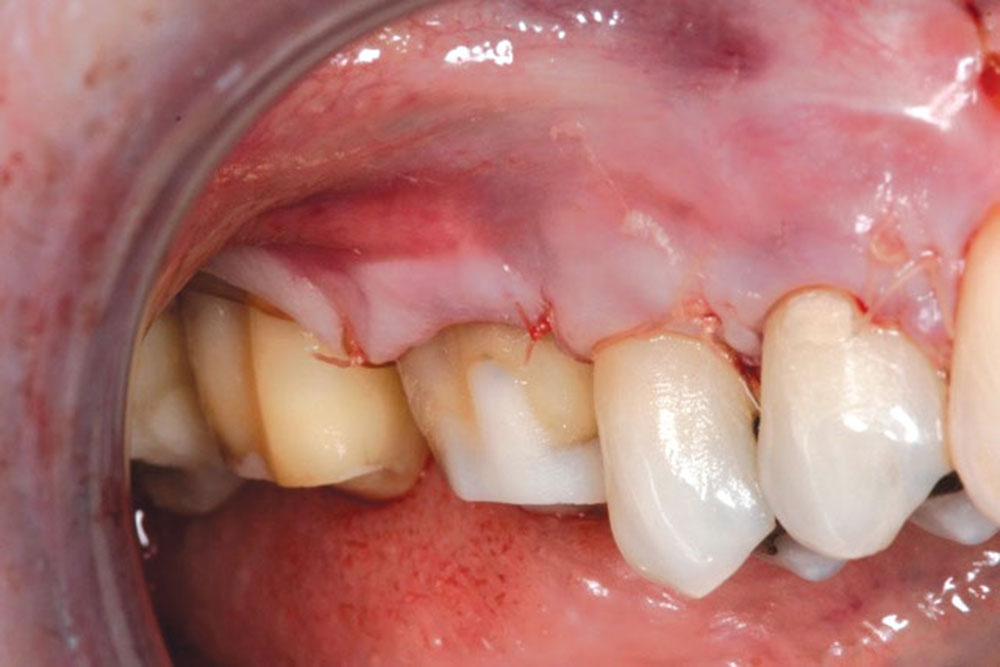
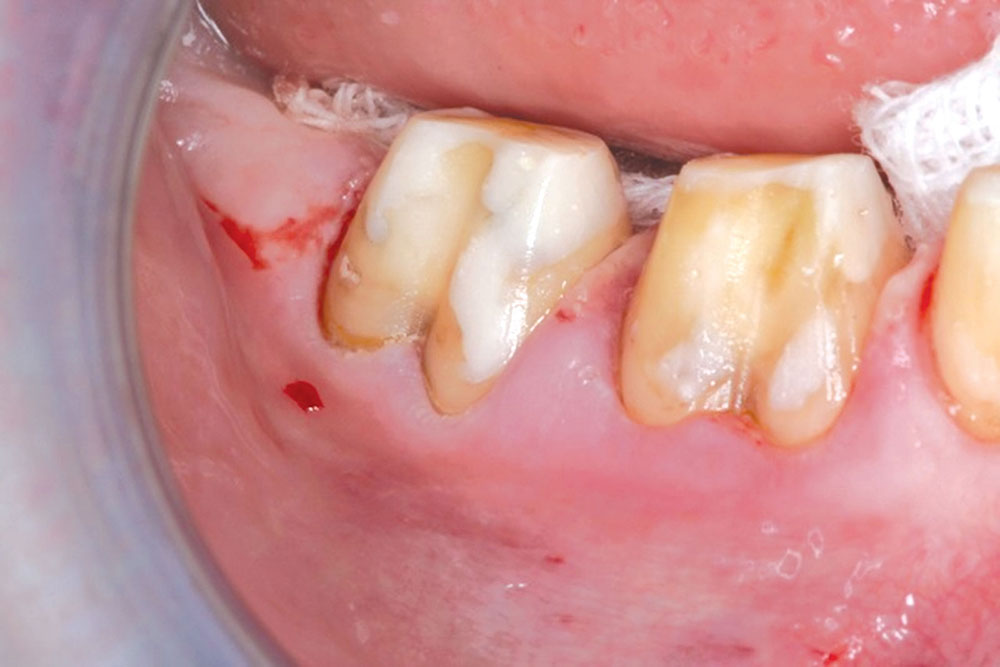
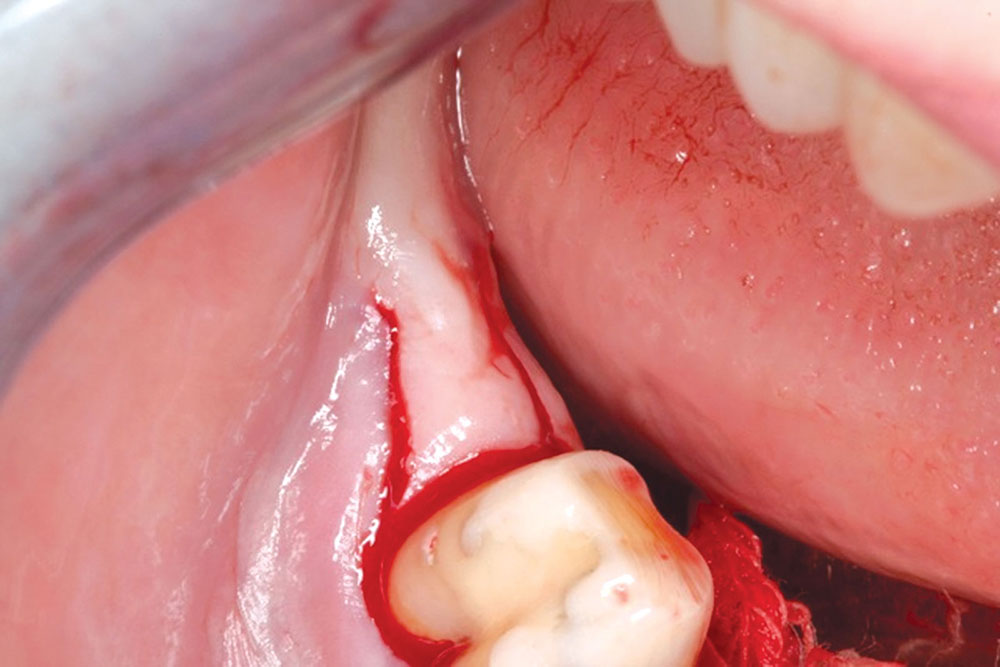
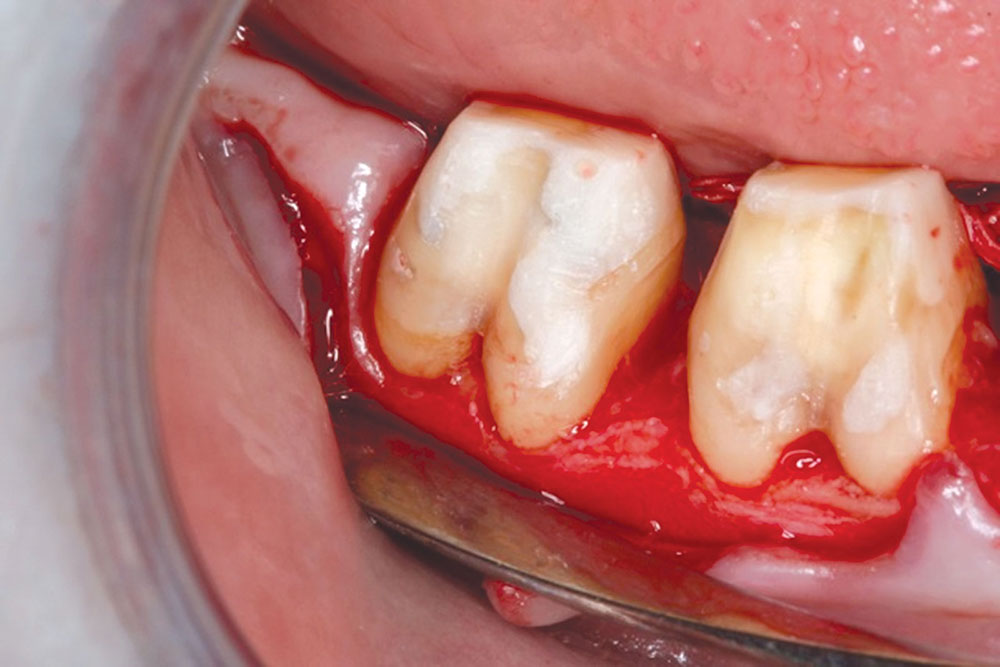
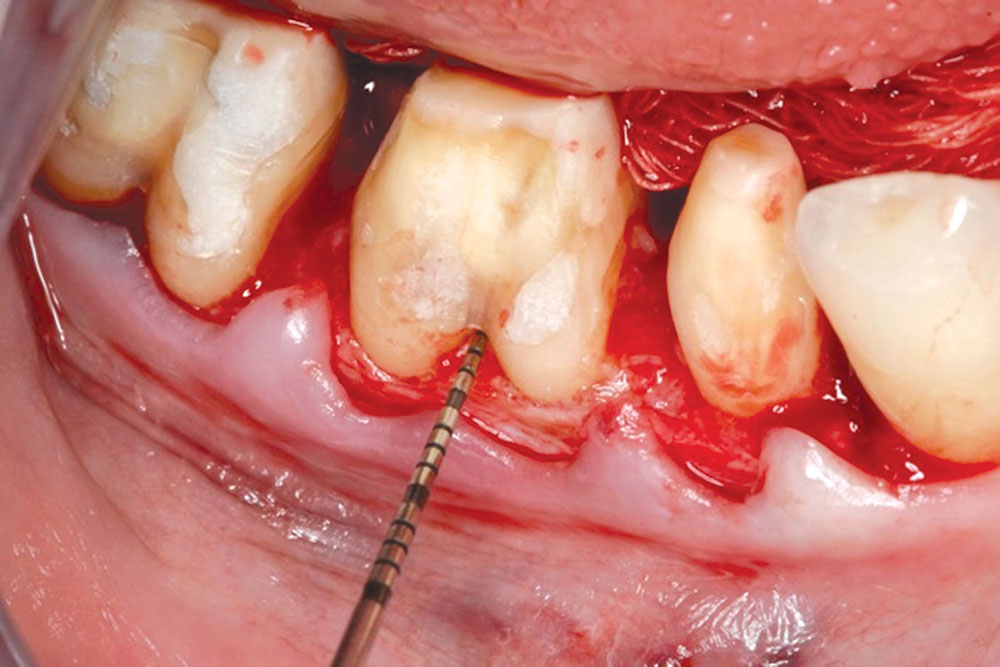
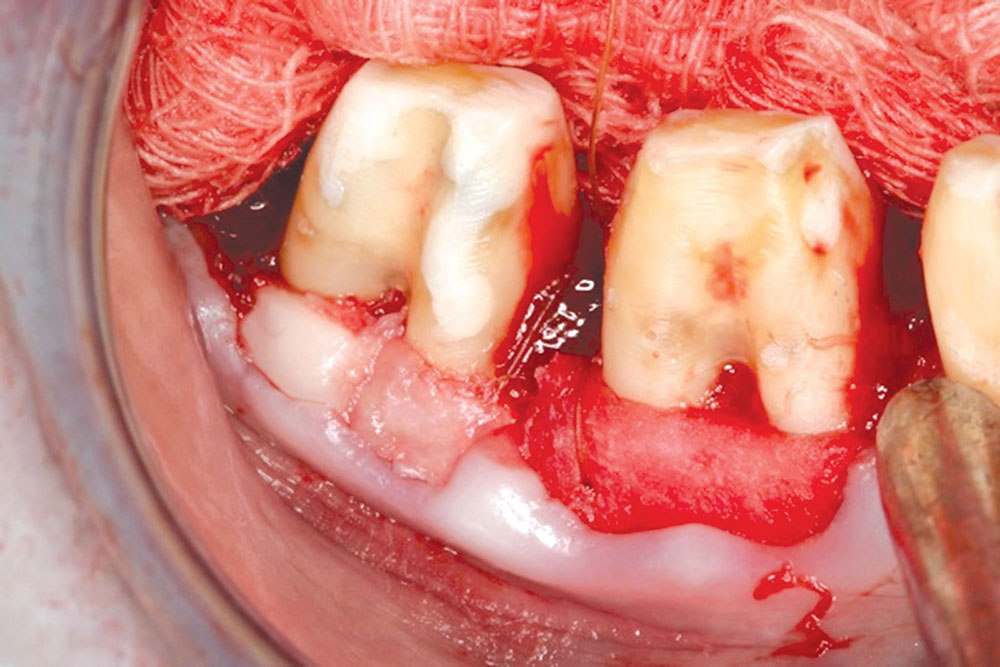
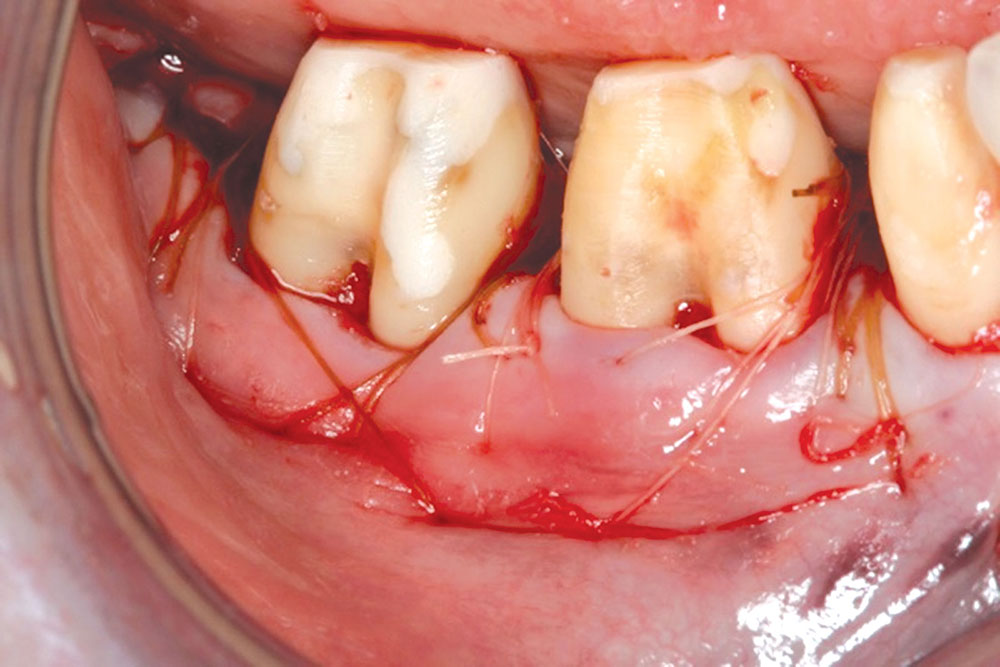
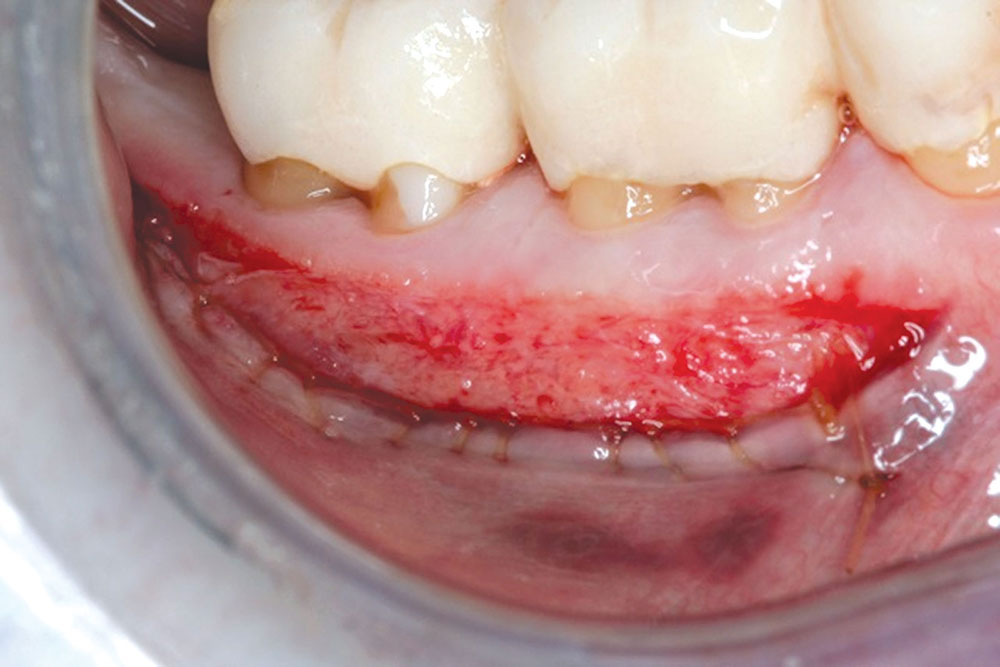
CASE 1
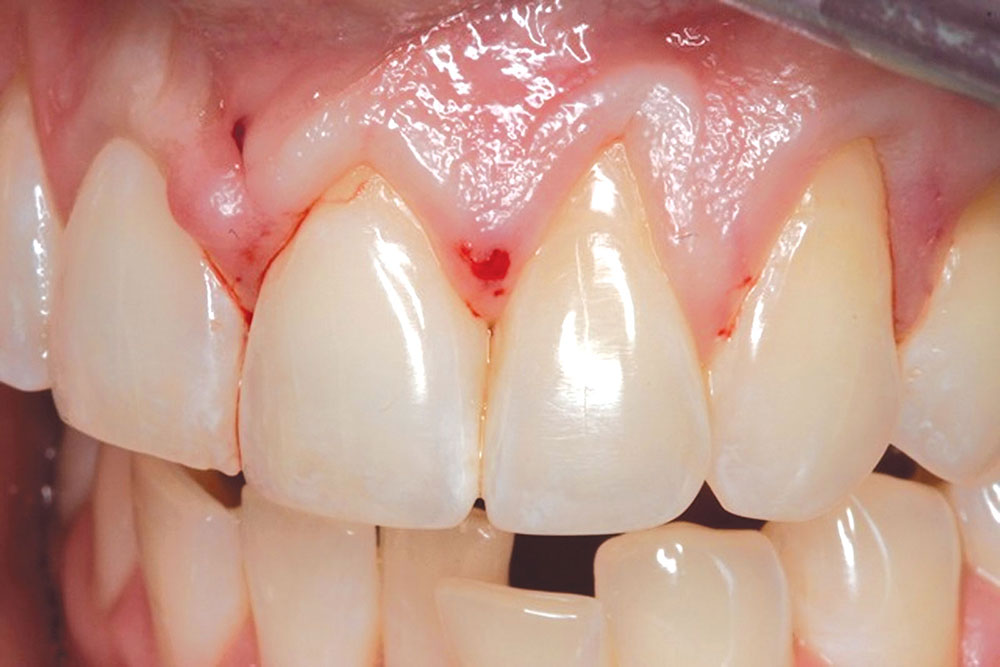
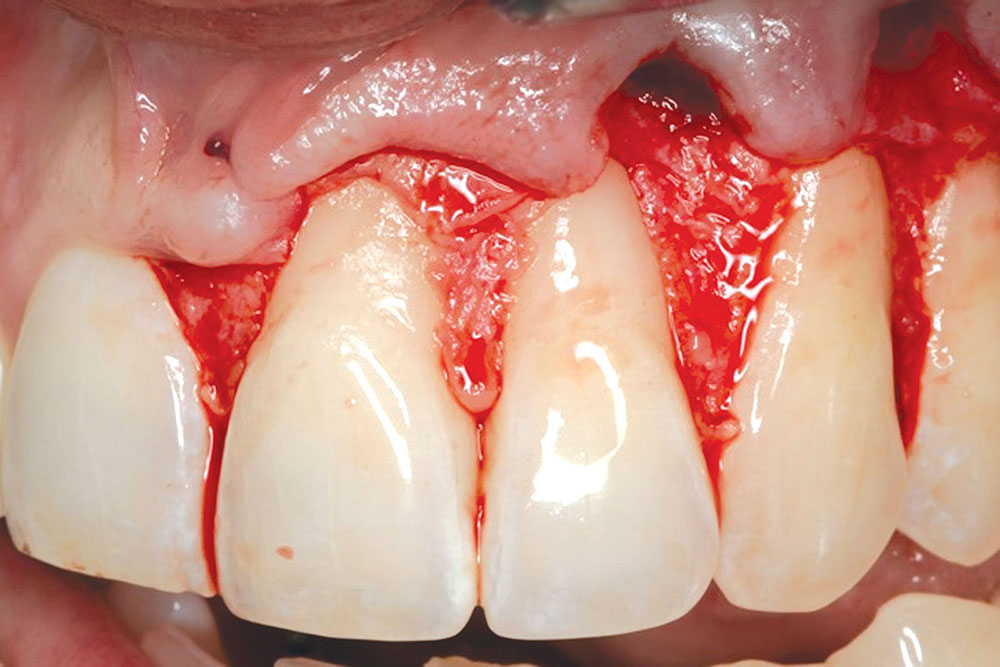
CASE 2
CASE 3
CASE 4
CASE 5
CASE 6
References
- AATB Standards for Tissue Banking, American Association of Tissue Banks, McLean, Va., aatb.org.
- Current Policies and Procedures of MTF, Musculoskeletal Transplant Foundation, Edison, N.J., mtf.org.
- Sullivan HC, Atkins JH. Free autogenous gingival grafts. 3. Utilization of grafts in the treatment of gingival recession. Periodontics. 1968 Aug;6(4):152-60.
- Khuller N. Coverage of gingival recession using tunnel connective tissue graft technique. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2009 May;13(2):101-5.
- Allen EP. Subpapillary continuous sling suturing method for soft tissue grafting with the tunneling technique. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010 Oct;30(5):479-85.
- Melker DJ. Biologic shaping from a restorative perspective. Chairside. 2013;8(1):64-8.
- Melker DJ. Periodontal photo essay. Chairside. Summer 2010;5(3):50-4.
- Melker DJ. Biologic shaping. Chairside. Spring 2010;5(2):39-42.
- Melker DJ, Richardson CR. Root reshaping: an integral component of periodontal surgery. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2001 Jun;21(3):296-304.
- Tucker LM, Melker DJ, Chasolen HM. Combining perio-restorative protocols to maximize function. Gen Dent. 2012 Jul-Aug;60(4):280-7.
Dr. Daniel Melker is in private practice in Clearwater, Florida, and lectures nationwide on periodontics and prosthodontics. Contact him at 727-725-0100.