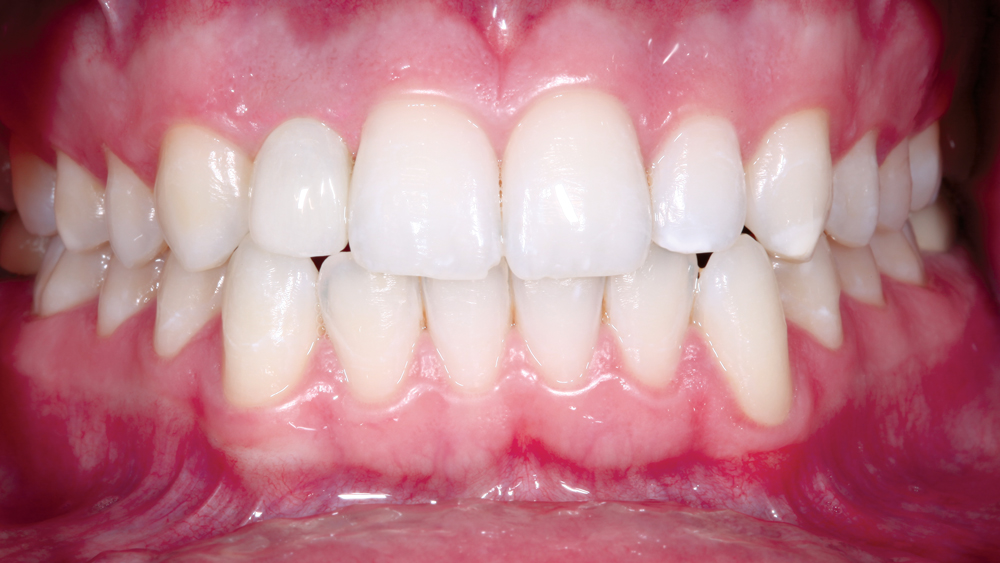
Clinical Benefits of Digitally Guided Implant Surgery
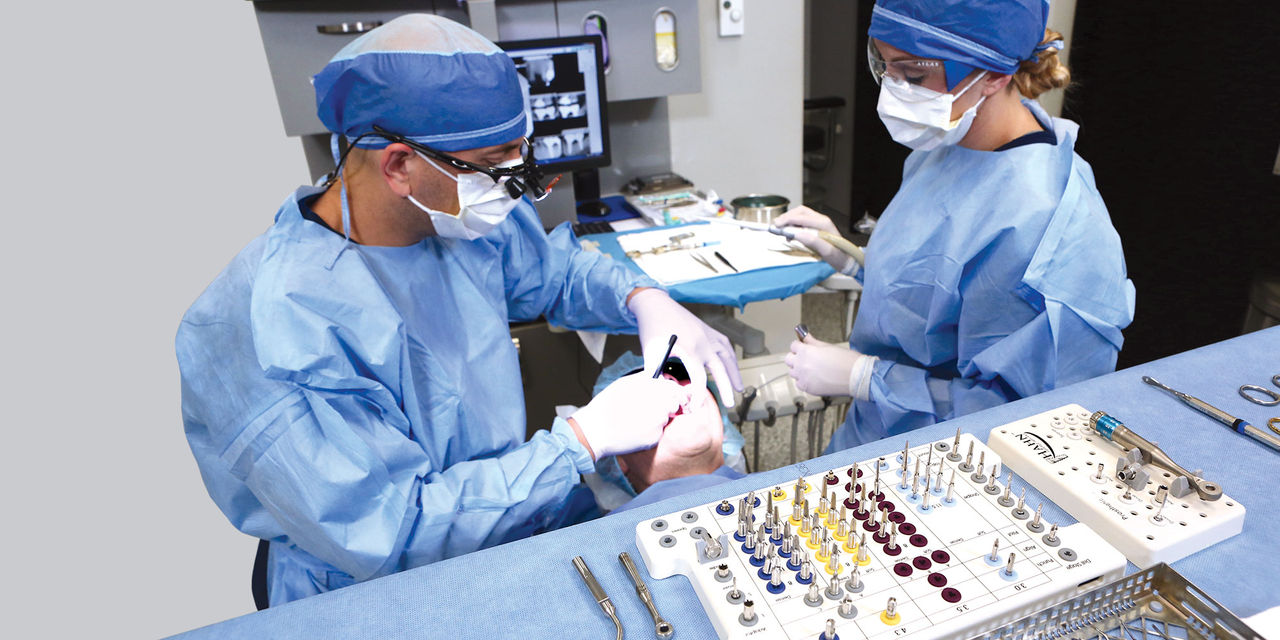
Note: The Hahn Tapered Implant System is now known as the Glidewell HT Implant System
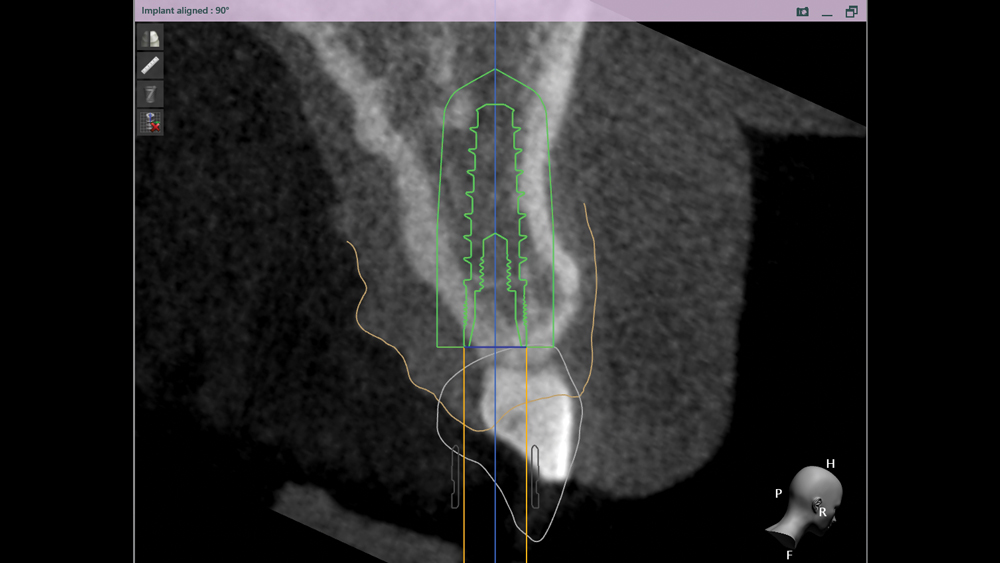
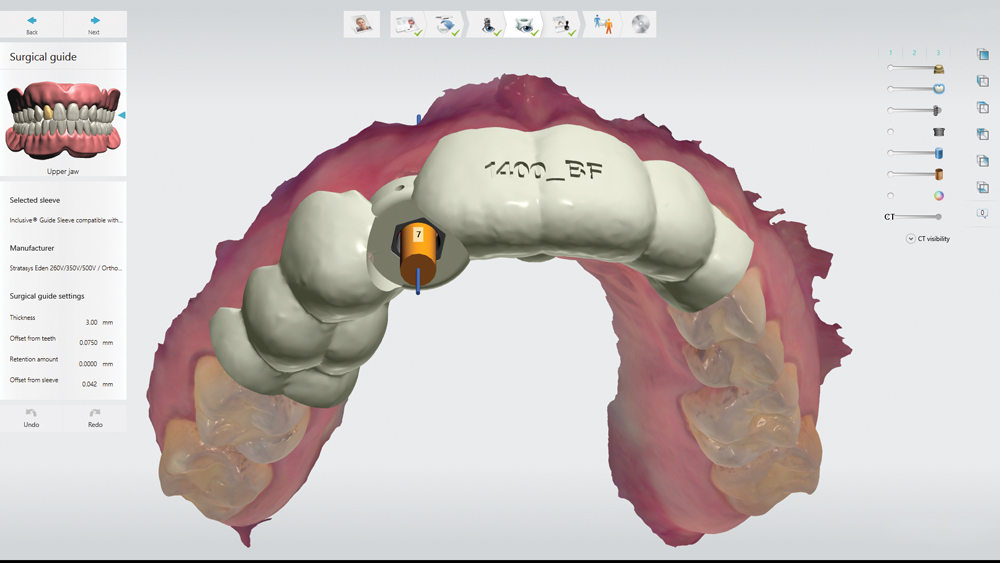
The benefits of CBCT scanning, digital treatment planning and digitally guided implant surgery are well-established. After determining the ideal implant position based on a 3D scan and the restorative goals, a surgical guide is fabricated to precisely transfer the digital treatment plan to the patient’s mouth. The surgical procedure is completed with great efficiency, reducing the chair time required to place an implant. Due to the clinical advantages of this approach, digitally guided surgery is utilized both by experienced practitioners seeking to optimize their results and by newcomers to implant placement, who benefit from increased safety and confidence.
Advantages of Guided Surgery
- Faster implant surgery reduces morbidity and fress up chair time
- Less invasive surgical procedure
- Faster healing time
- Improved precision and predictability
- Can help avoid nearby patient anatomy and accomodate limited bone volume
- Option of immediate loading with prefabricated provisional
THE HAHN™ TAPERED IMPLANT GUIDED SURGERY SYSTEM
With the recent release of the Hahn™ Guided Surgery System (Glidewell Direct; Irvine, Calif.), clinicians can now place Hahn Tapered Implants at a digitally predetermined position, affording a high degree of precision and confidence. The Hahn Guided Surgery System includes a streamlined surgical protocol that enables clinicians at all experience levels to efficiently deliver Hahn Tapered Implants, which excel at achieving high primary stability in a wide variety of clinical situations.
Clinicians can now place Hahn Tapered Implants at a digitally predetermined position, affording a high degree of precision and confidence.
Advantages of Hahn Guided Surgery System
- Streamlined surgical protocol
- Drills are diameter-specific and include depth stops
- All-in-one surgical kit suitable for virtually any case
- Entire procedure is performed through a surgical guide
- Easy-to-follow drilling sequence
- Affordable treatment costs
- Minimal instrumentation required
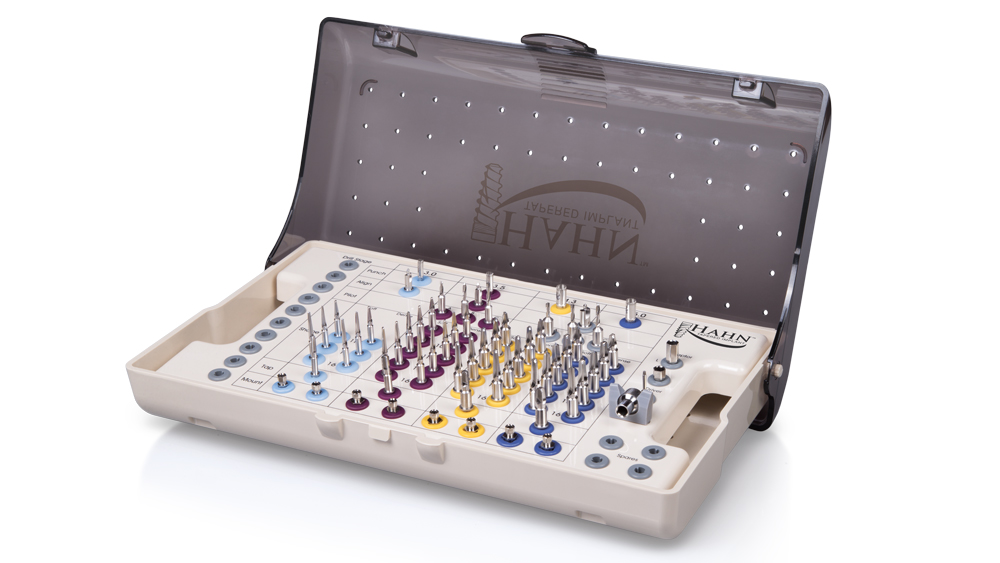
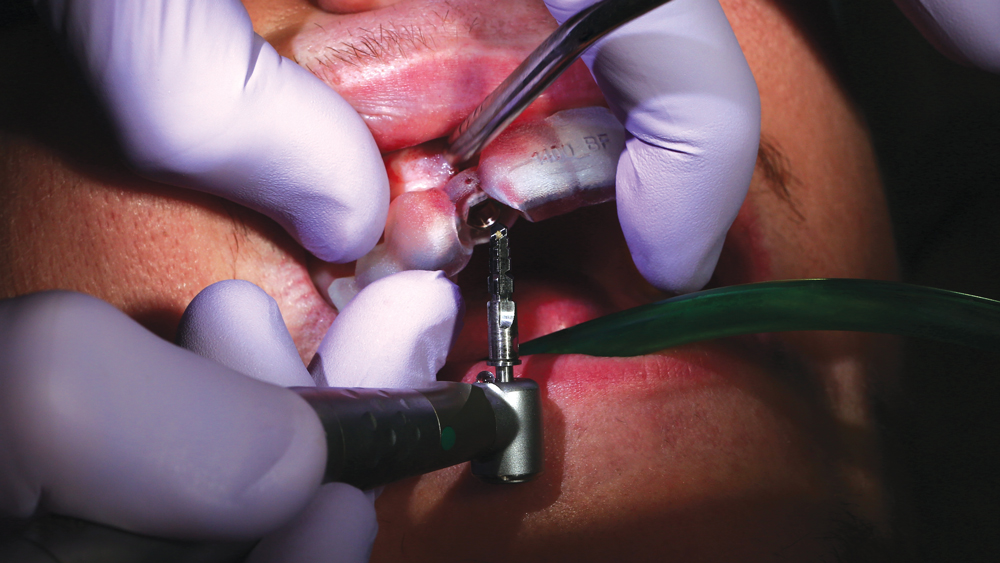
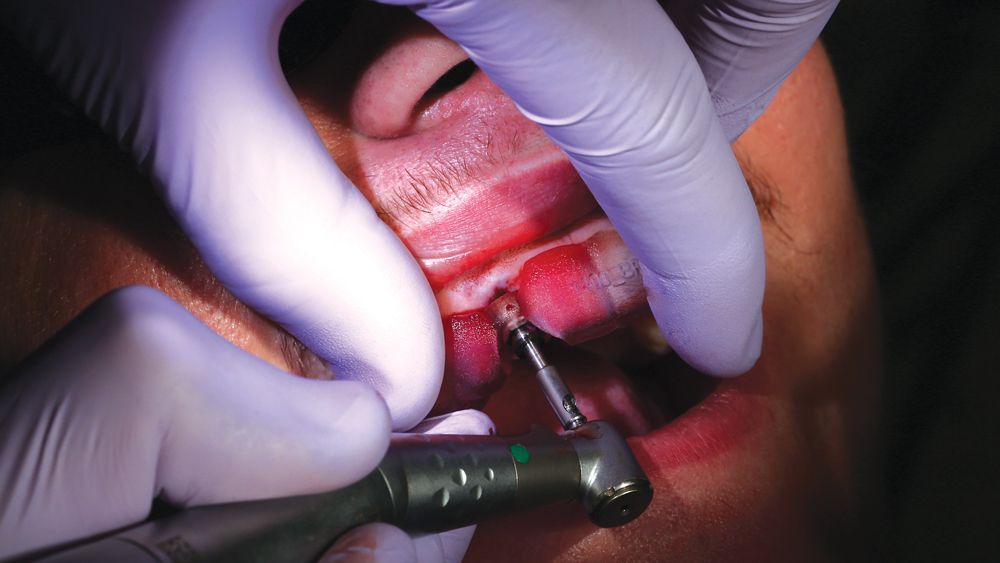
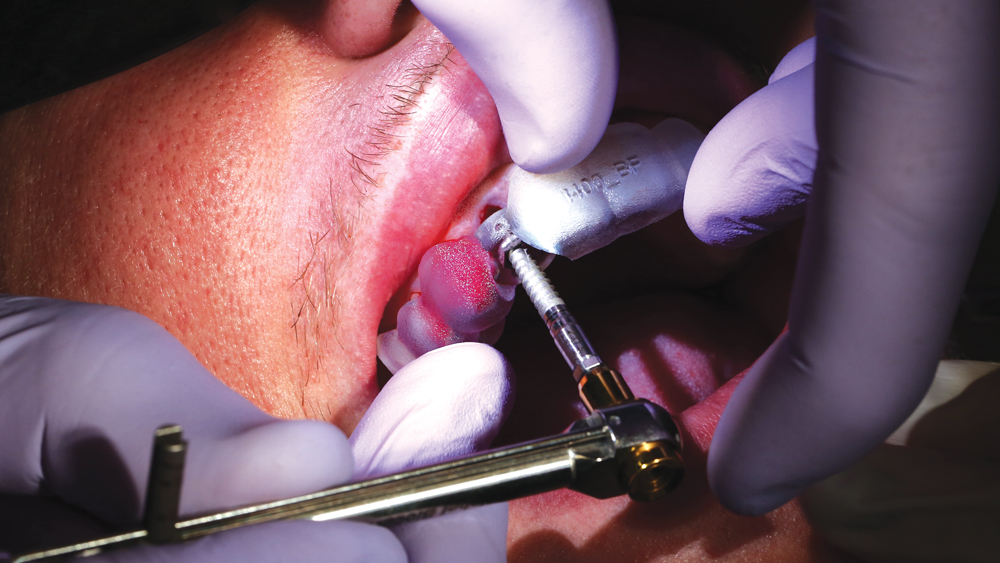
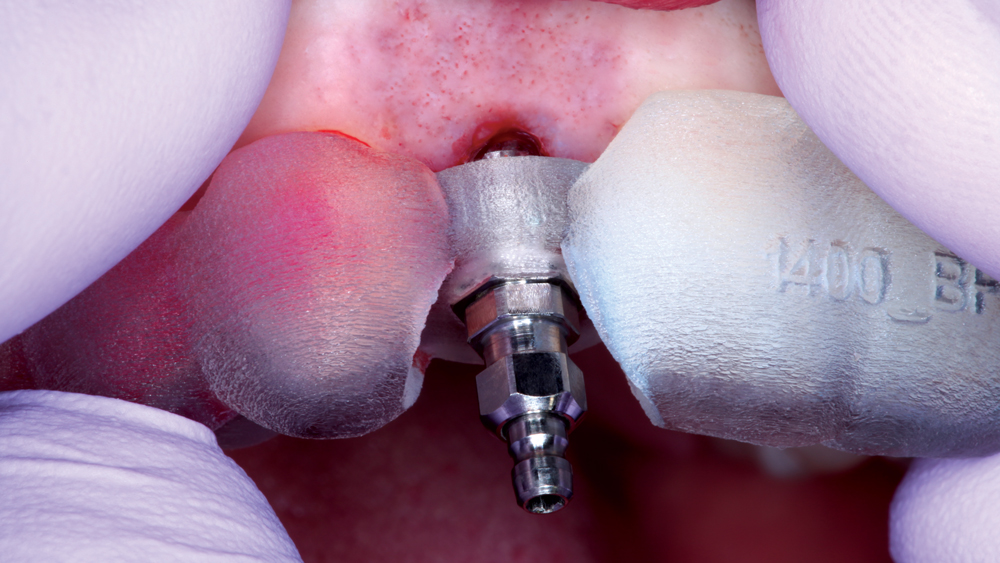
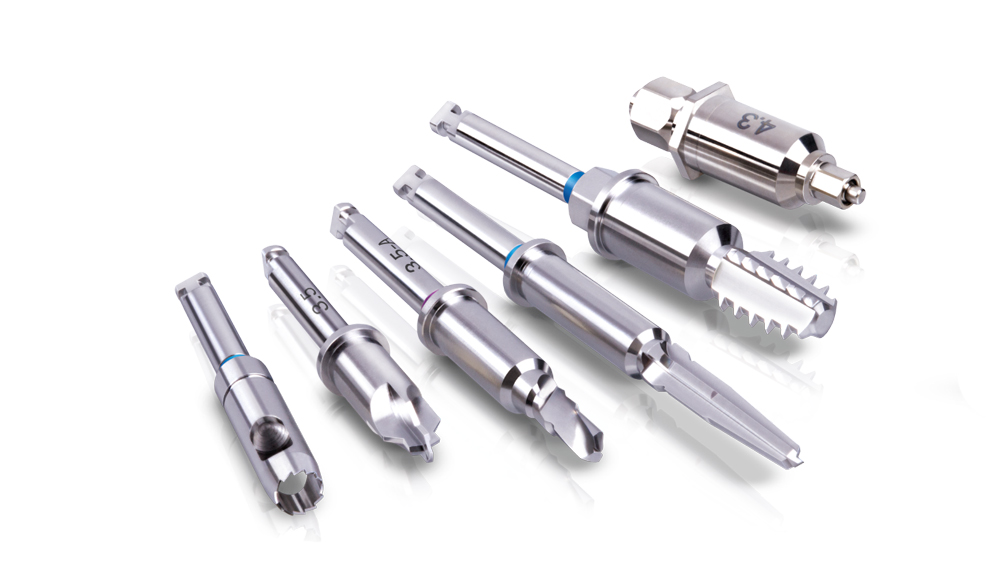
The Hahn Guided Surgical Kit (Glidewell Direct) has been designed to eliminate the need for drill keys, inserts or “spoons” commonly found in other guided surgery systems. The surgical kit’s efficient, straightforward sequence of drills creates an osteotomy in the exact shape, diameter and length of the prescribed implant, ensuring the implant ends up in the exact position determined by the digital treatment plan. Further, the entire surgical procedure, from the initial osteotomy to implant placement, is performed through the surgical guide. Whether using the Digital Treatment Planning service of Glidewell Laboratories or another source for surgical guides, specific guide sleeves are provided to enable practitioners to perform the entire surgical procedure with an efficient and fully guided protocol.

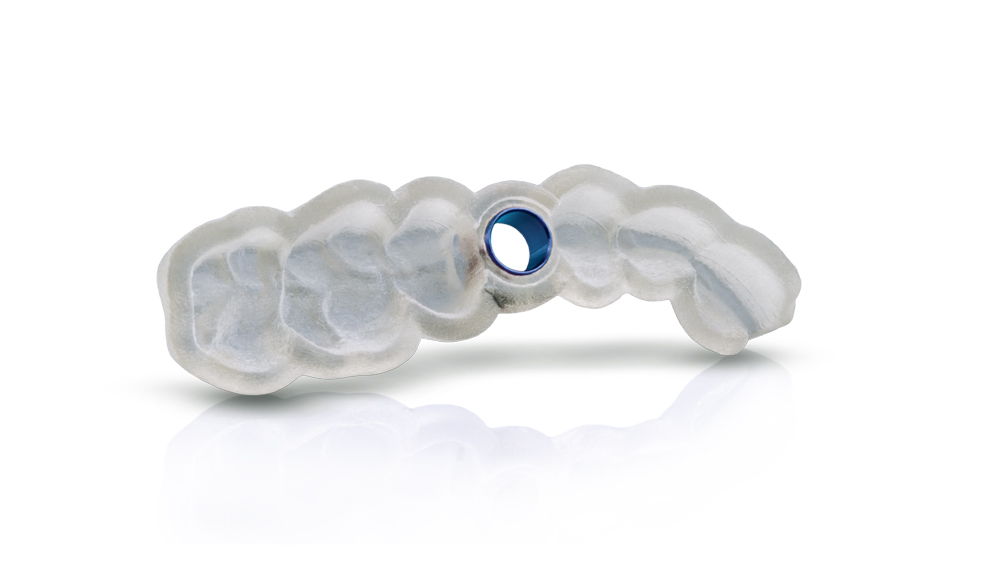
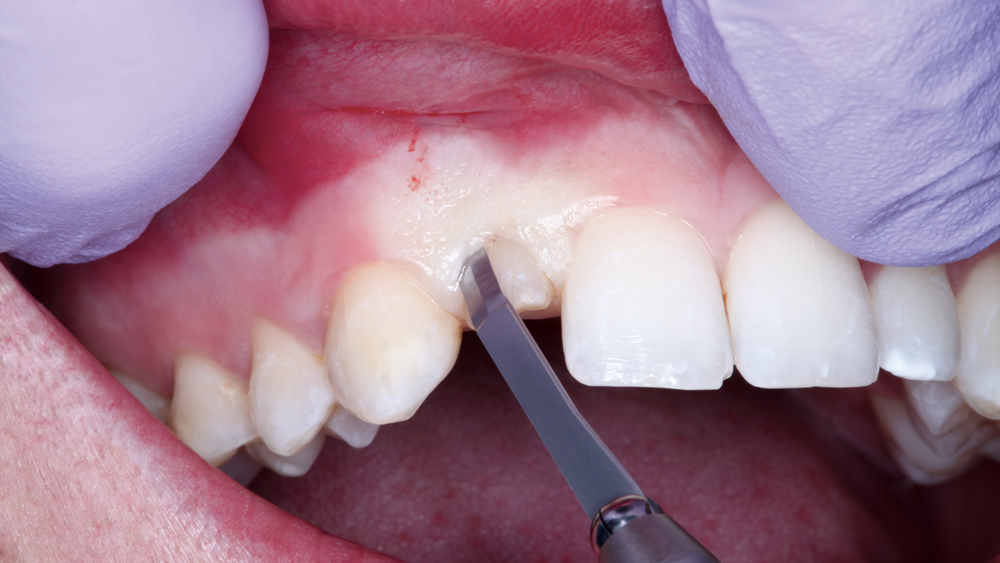
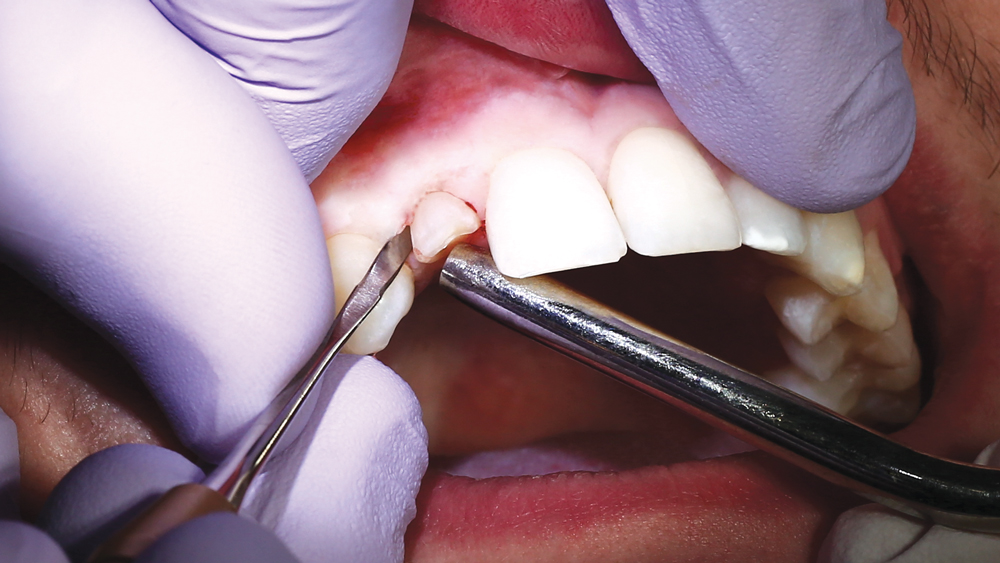
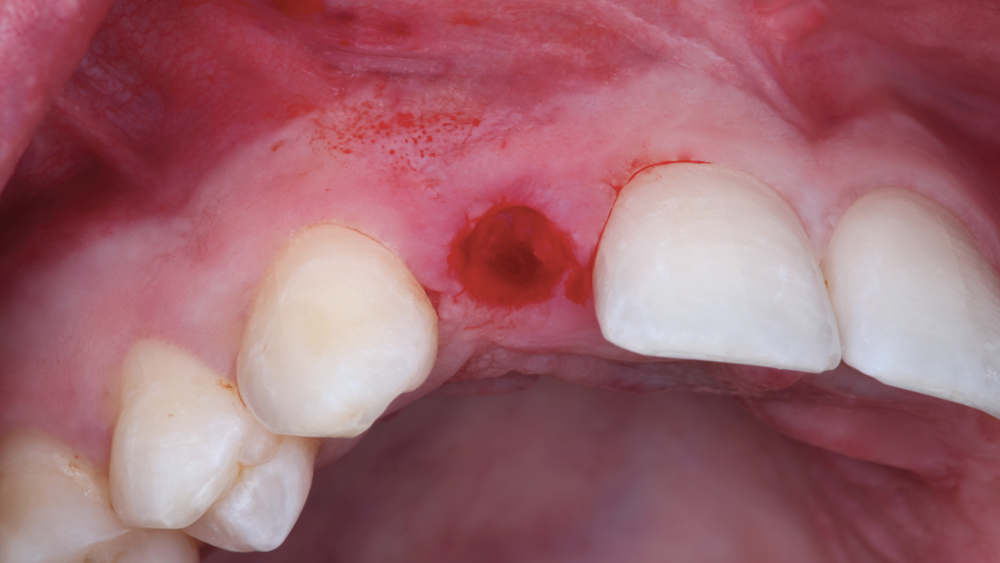
CASE REPORT
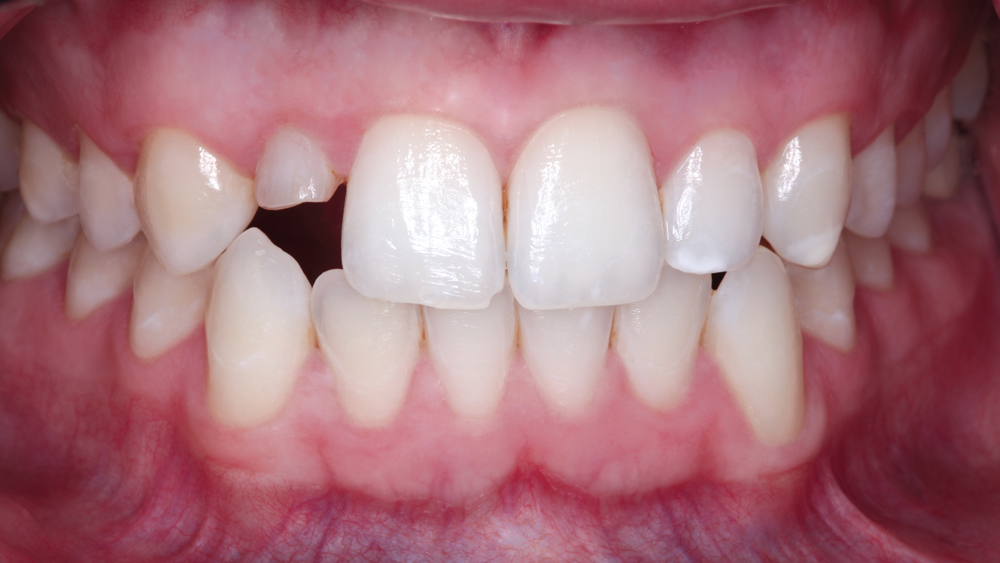
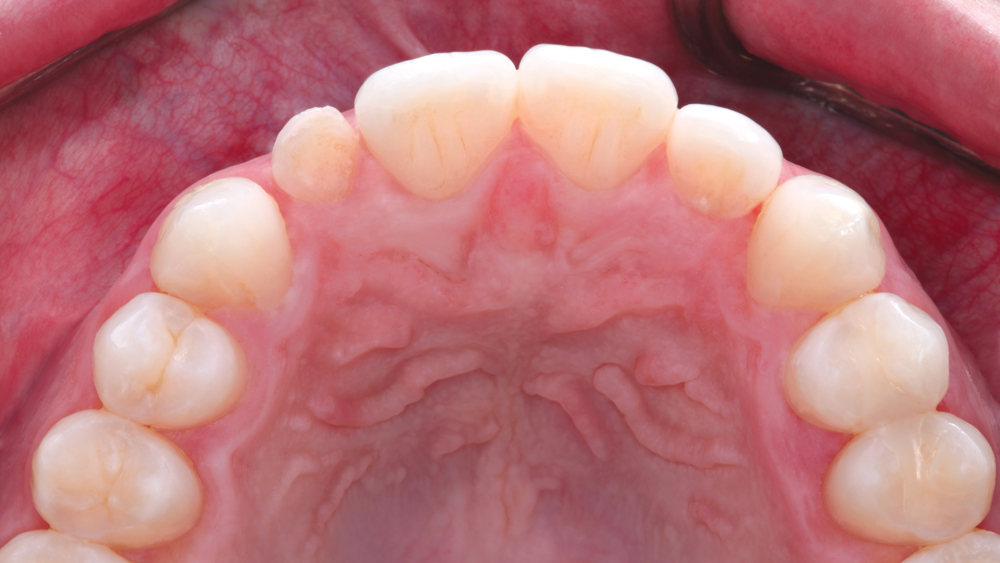
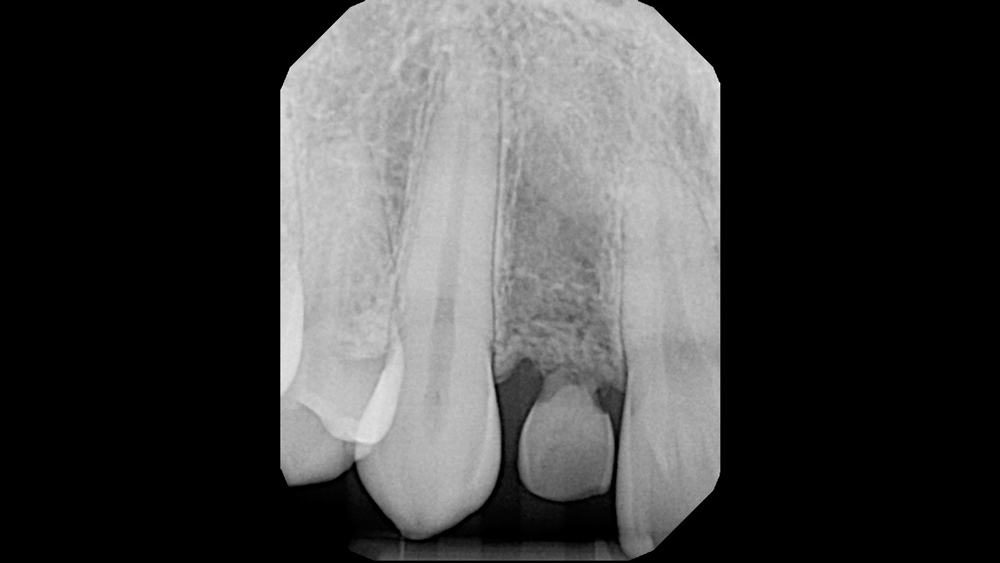
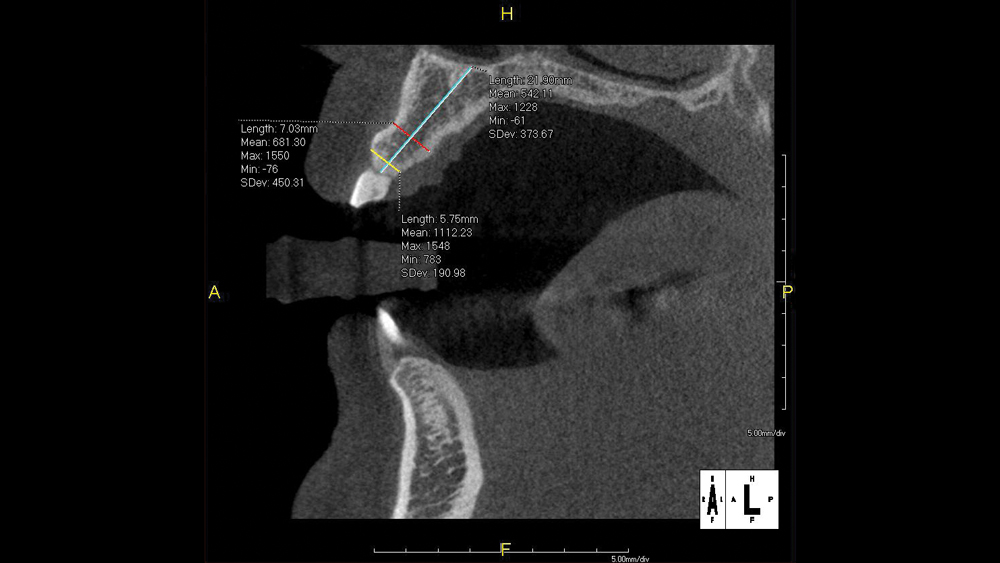
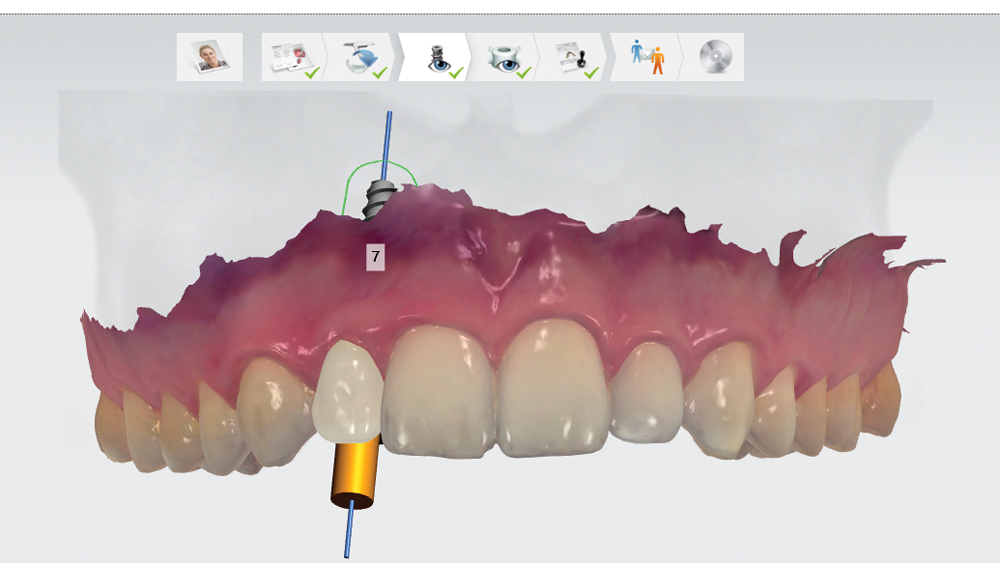
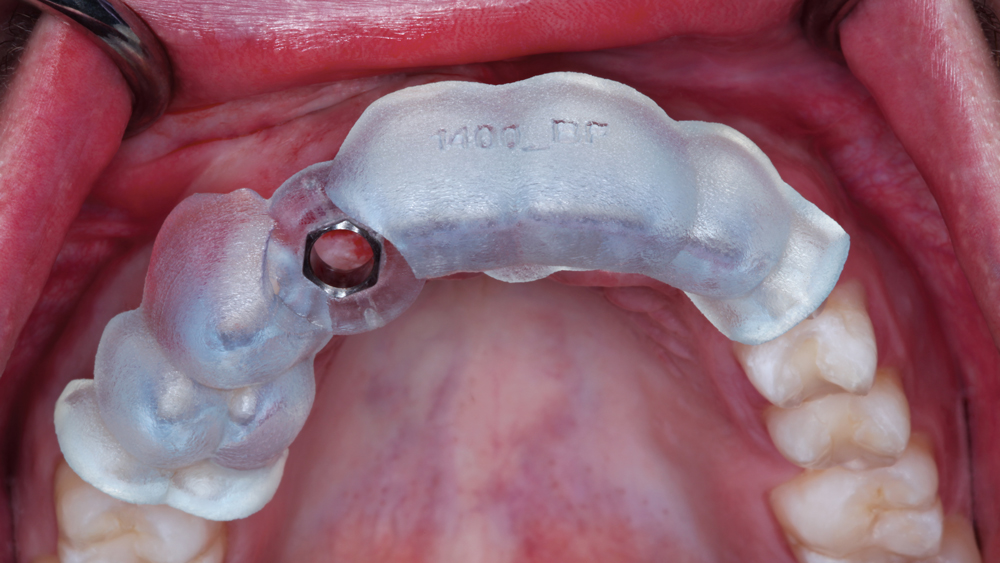
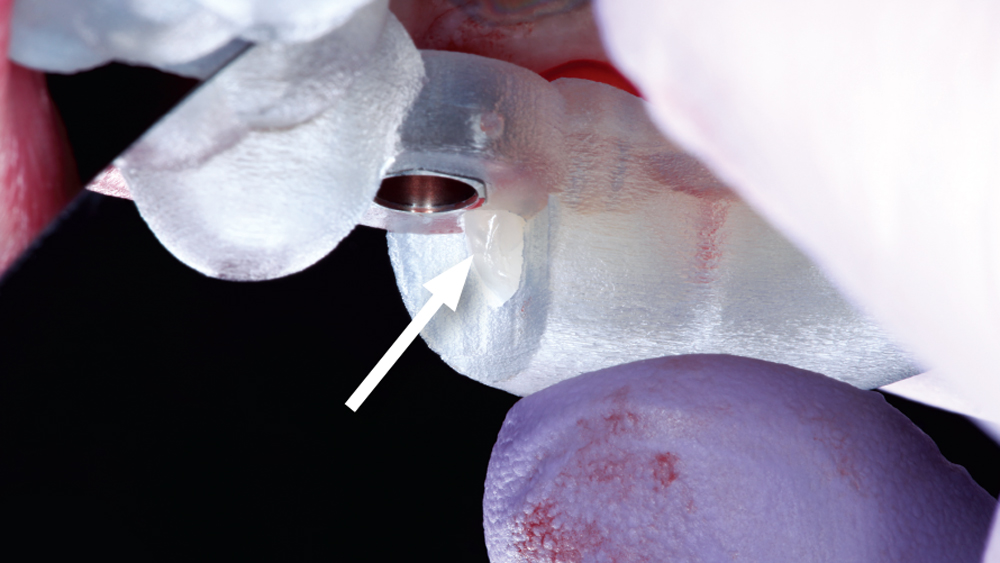
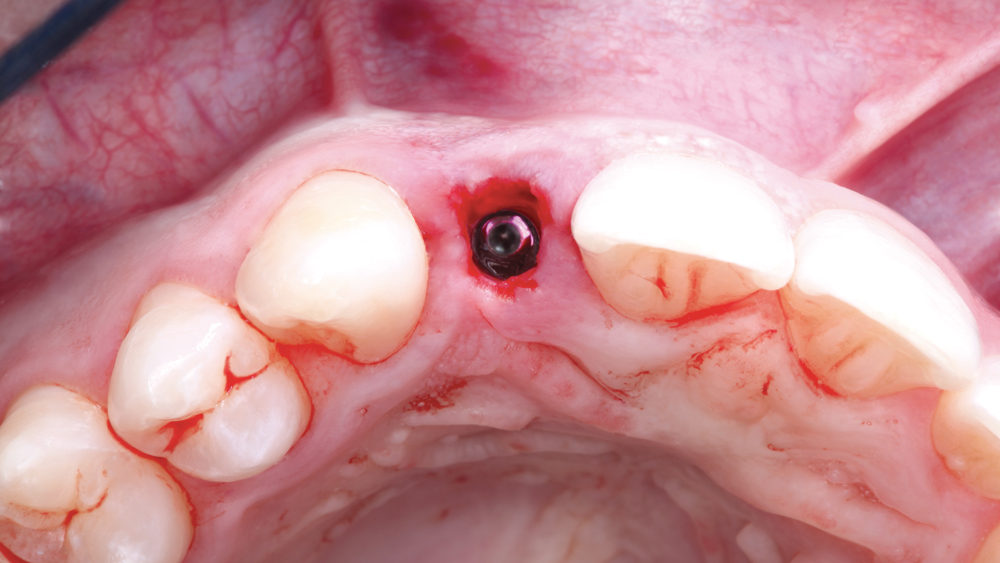
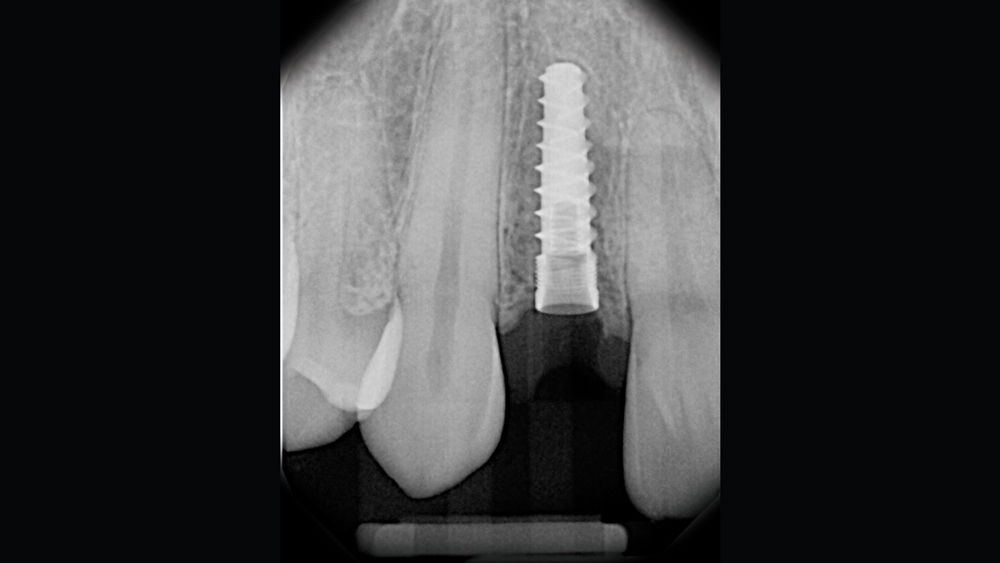
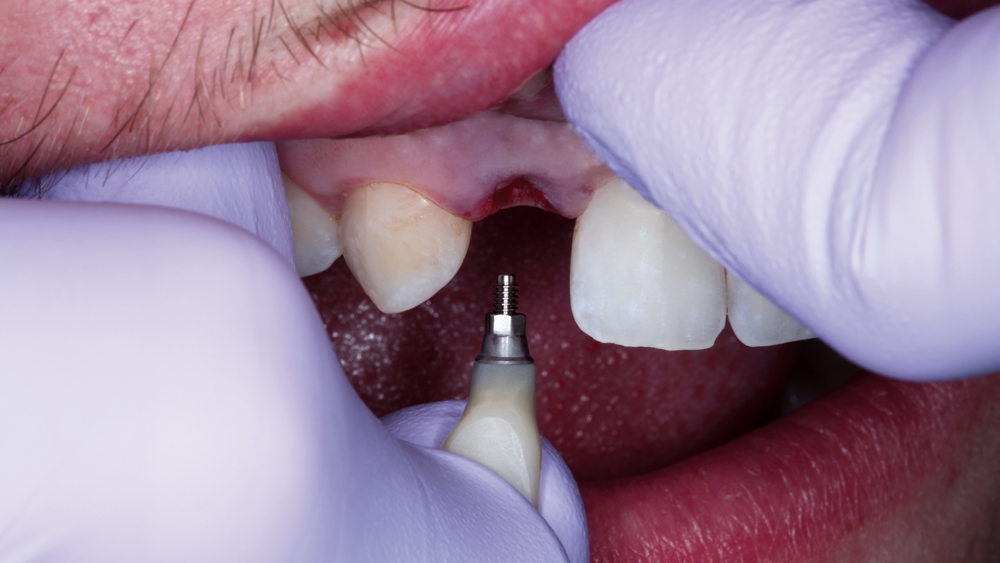
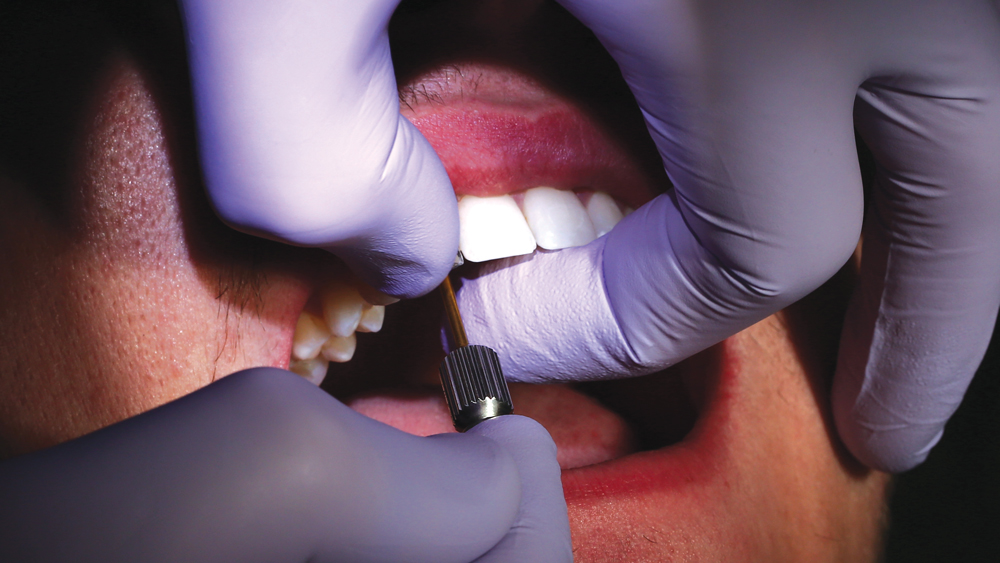
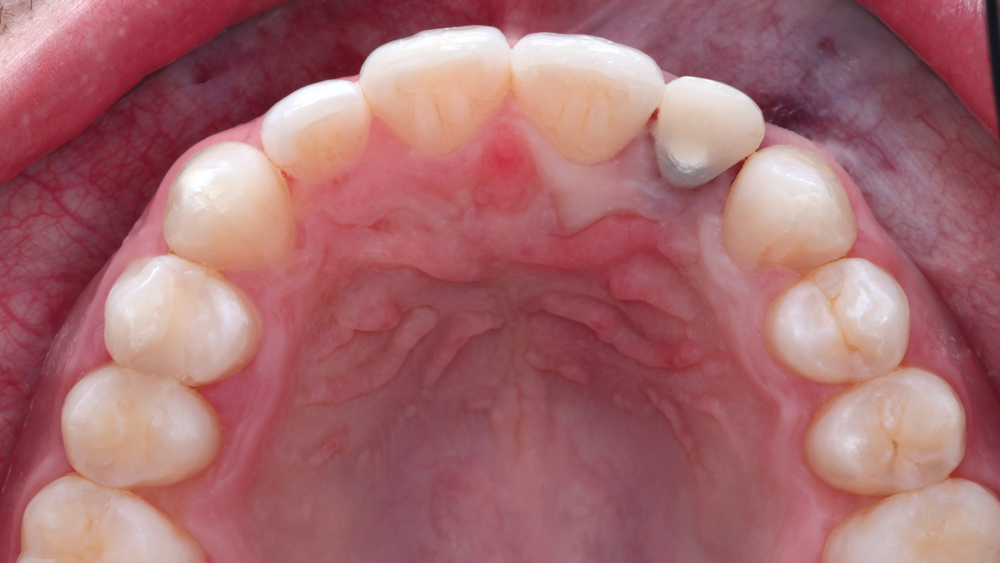
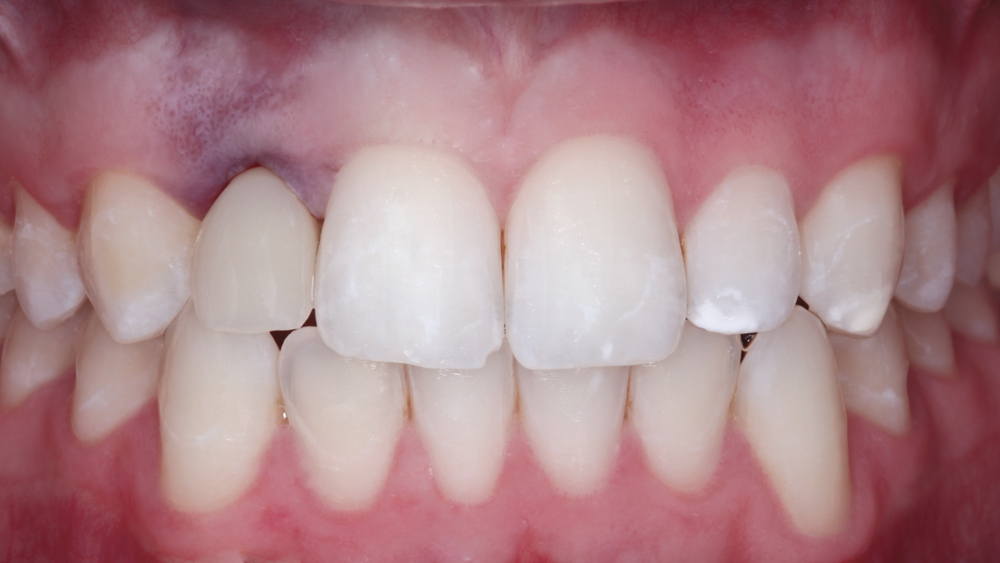
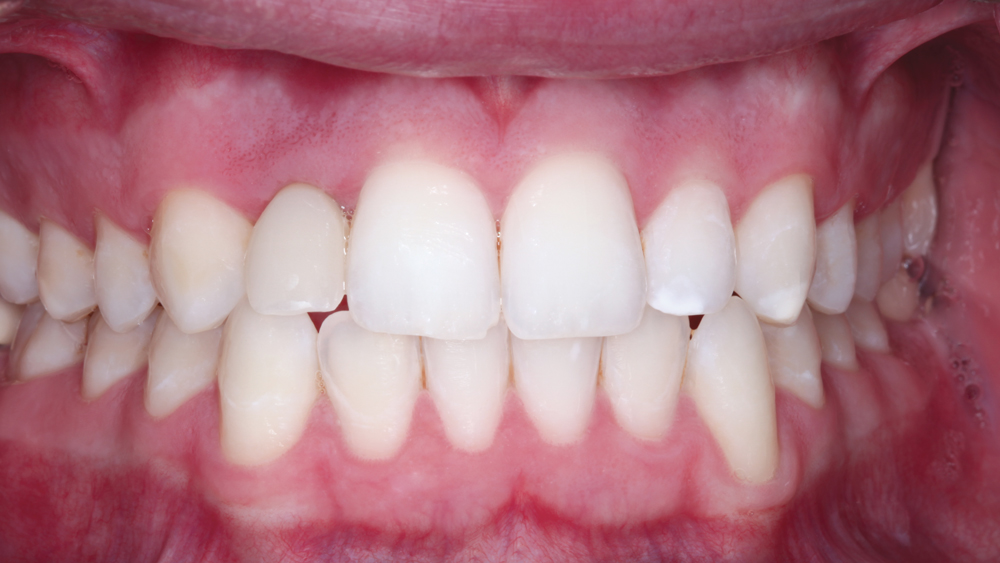
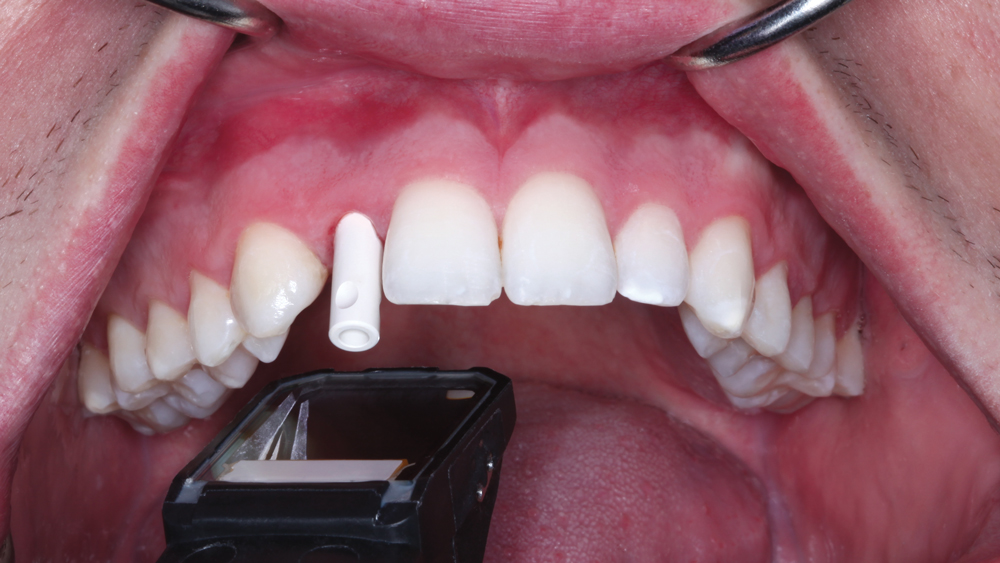
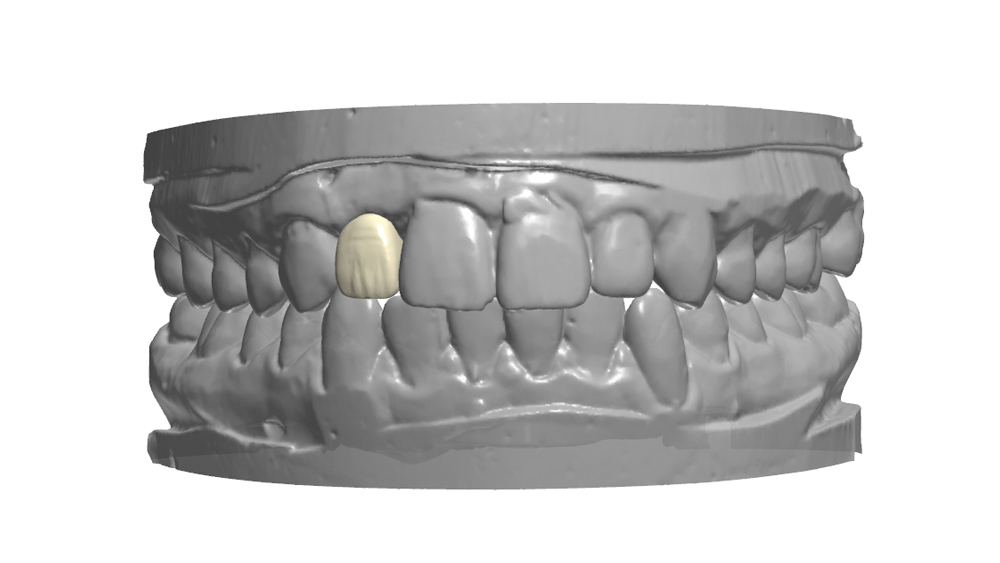
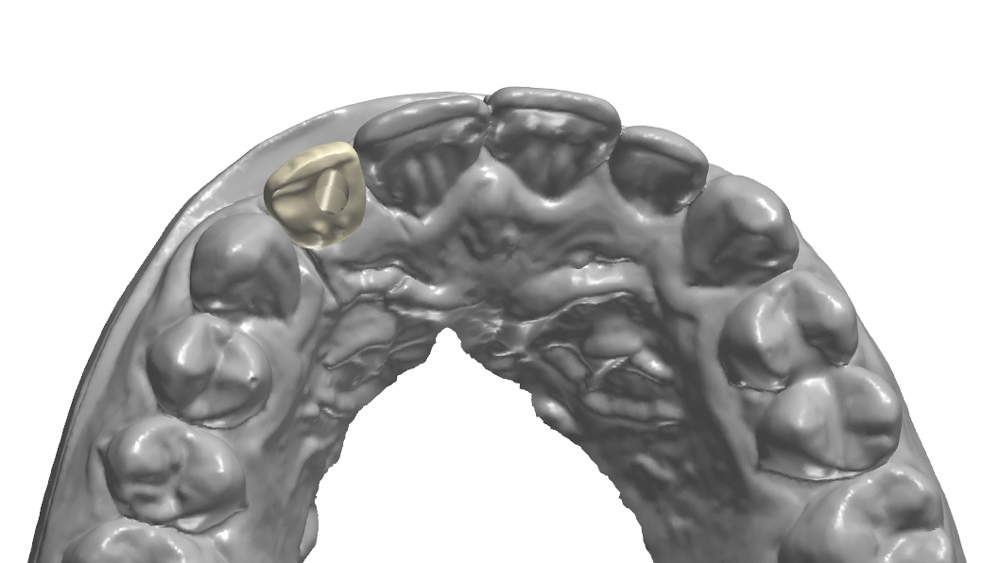
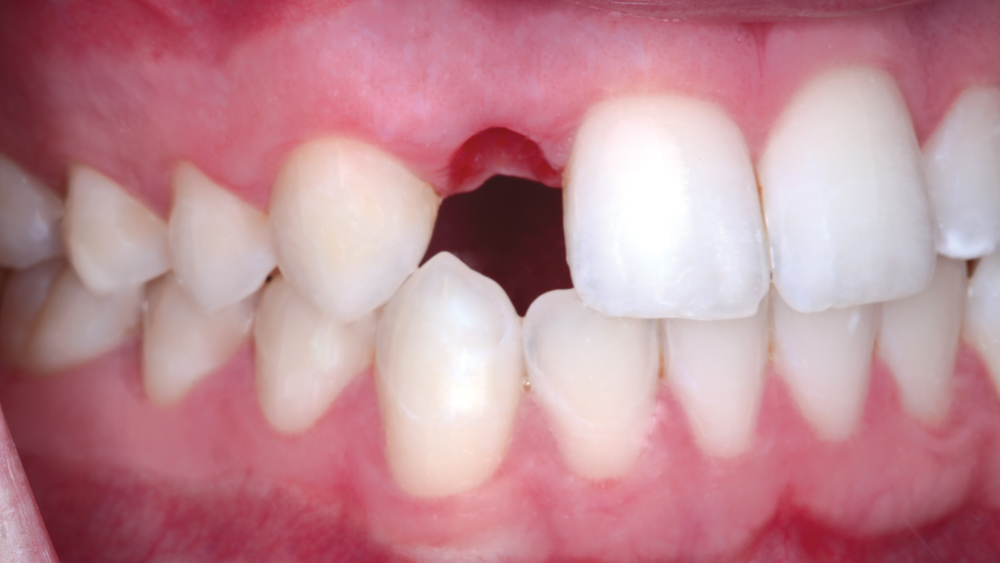
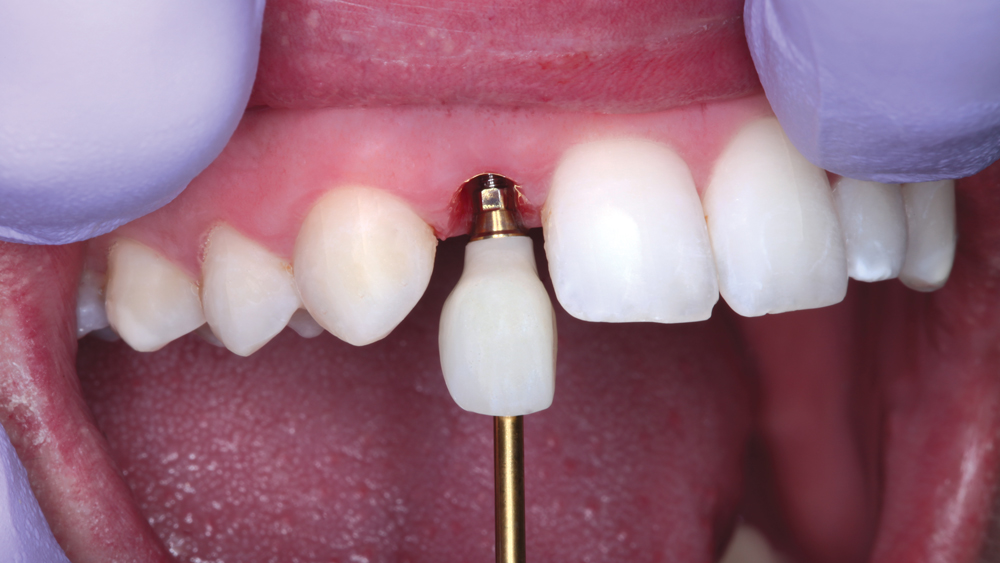
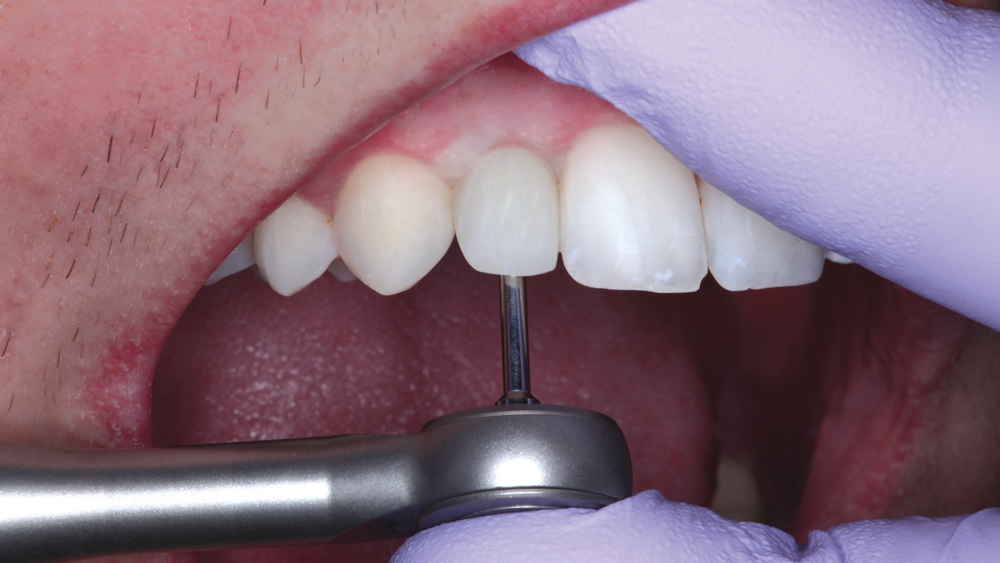
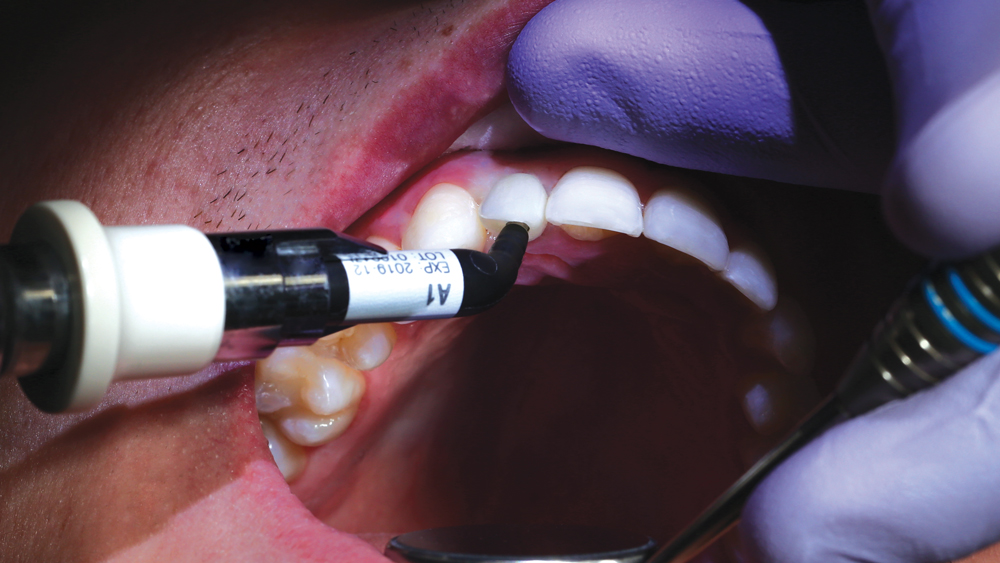
The following case illustrates the efficient, straightforward clinical workflow for placing Hahn Tapered Implants via guided surgery. A digital treatment plan is developed in which a 3.5 mm implant is positioned to support the ideal prosthetic outcome. An immediate provisional crown is designed in concert with the surgical guide and delivered at the time of surgery, helping to produce a predictable, highly esthetic restoration for a demanding case in the smile zone.
CONCLUSION
With the release of the Hahn Guided Surgery System, clinicians now have an efficient option for the digitally guided surgical placement of Hahn Tapered Implants. With simplified instrumentation, a streamlined surgical protocol, and support from a dental lab that ensures a restorative-driven approach is maintained throughout the course of treatment, the Hahn Guided Surgery System is a valuable tool for novice and experienced implant practitioners alike.